ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(7):813-824. doi:10.7150/ijbs.11797 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Functional Analysis of a c-di-AMP-specific Phosphodiesterase MsPDE from Mycobacterium smegmatis
State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, Hubei 430070, PR China
Abstract
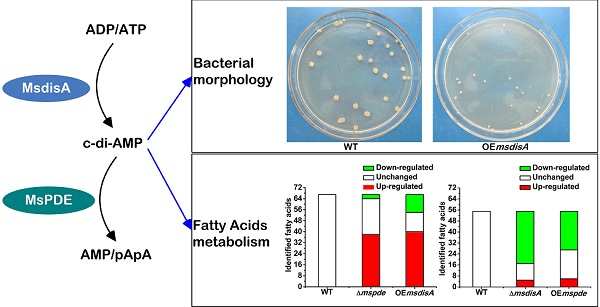
Cyclic di‑AMP (c-di-AMP) is a second signaling molecule involved in the regulation of bacterial physiological processes and interaction between pathogen and host. However, the regulatory network mediated by c-di-AMP in Mycobacterium remains obscure. In M. smegmatis, a diadenylate cyclase (DAC) was reported recently, but there is still no investigation on c-di-AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE). Here, we provide a systematic study on signaling mechanism of c-di-AMP PDE in M. smegmatis. Based on our enzymatic analysis, MsPDE (MSMEG_2630), which contained a DHH-DHHA1 domain, displayed a 200-fold higher hydrolytic efficiency (kcat/Km) to c-di-AMP than to c-di-GMP. MsPDE was capable of converting c-di-AMP to pApA and AMP, and hydrolyzing pApA to AMP. Site-directed mutations in DHH and DHHA1 revealed that DHH domain was critical for the phosphodiesterase activity. To explore the regulatory role of c-di-AMP in vivo, we constructed the mspde mutant (Δmspde) and found that deficiency of MsPDE significantly enhanced intracellular C12-C20 fatty acid accumulation. Deficiency of DAC in many bacteria results in cell death. However, we acquired the M. smegmatis strain with DAC gene disrupted (ΔmsdisA) by homologous recombination approach. Deletion of msdisA reduced bacterial C12-C20 fatty acids production but scarcely affected bacterial survival. We also provided evidences that superfluous c-di-AMP in M. smegmatis could lead to abnormal colonial morphology. Collectively, our results indicate that MsPDE is a functional c-di-AMP-specific phosphodiesterase both in vitro and in vivo. Our study also expands the regulatory network mediated by c-di-AMP in M. smegmatis.
Keywords: cyclic di‑AMP, Mycobacterium smegmatis, phosphodiesterase, diadenylate cyclase, fatty acids
