ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(1):87-99. doi:10.7150/ijbs.13229 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Retinoic Acid Induced-Autophagic Flux Inhibits ER-Stress Dependent Apoptosis and Prevents Disruption of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier after Spinal Cord Injury
1. Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, 325035 China
2. Molecular Pharmacology Research Center, School of Pharmacy, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, 325035 China
3. Department of Bioengineering and the McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15219, USA
4. Department of Neurosurgery, Cixi People's Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Ningbo, 315300, China
5. Department of Emergency, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325035, China
6. Department of Neurology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA.
7. Institute of Basic Medical Science, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
The first two authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
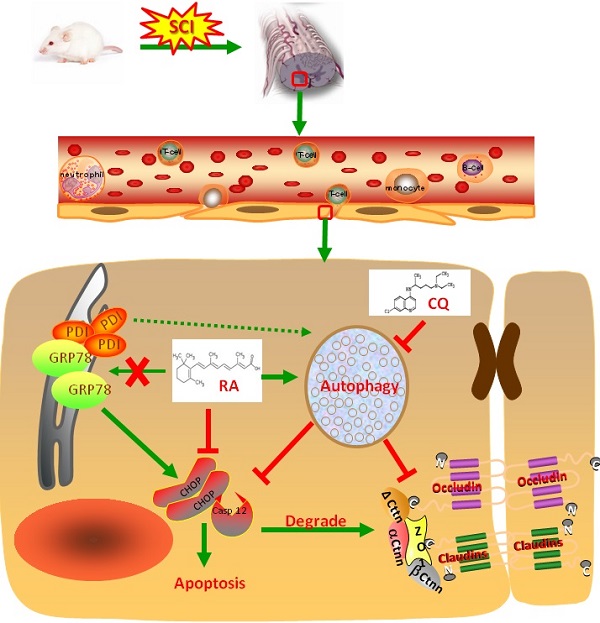
Spinal cord injury (SCI) induces the disruption of the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) which leads to infiltration of blood cells, an inflammatory response, and neuronal cell death, resulting spinal cord secondary damage. Retinoic acid (RA) has a neuroprotective effect in both ischemic brain injury and SCI, however the relationship between BSCB disruption and RA in SCI is still unclear. In this study, we demonstrated that autophagy and ER stress are involved in the protective effect of RA on the BSCB. RA attenuated BSCB permeability and decreased the loss of tight junction (TJ) molecules such as P120, β-catenin, Occludin and Claudin5 after injury in vivo as well as in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (BMECs). Moreover, RA administration improved functional recovery in the rat model of SCI. RA inhibited the expression of CHOP and caspase-12 by induction of autophagic flux. However, RA had no significant effect on protein expression of GRP78 and PDI. Furthermore, combining RA with the autophagy inhibitor chloroquine (CQ) partially abolished its protective effect on the BSCB via exacerbated ER stress and subsequent loss of tight junctions. Taken together, the neuroprotective role of RA in recovery from SCI is related to prevention of of BSCB disruption via the activation of autophagic flux and the inhibition of ER stress-induced cell apoptosis. These findings lay the groundwork for future translational studies of RA for CNS diseases, especially those related to BSCB disruption.
Keywords: blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB), retinoic acid (RA), autophagy, endocytoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, spinal cord injury (SCI)
