ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(6):701-709. doi:10.7150/ijbs.13635 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ribose Accelerates Gut Motility and Suppresses Mouse Body Weight Gaining
1. State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering and Institute of Developmental Biology and Molecular Medicine, National Center for International Research, Fudan-Yale Center for Biomedical Research, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2. Shanghai Yao Yuan Biotechnology (Drug Farm) Limited, Co. Room 701, 43 Handan Rd, Shanghai, 200437, China
3. Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Genetics, Yale University School of Medicine, Boyer Center for Molecular Medicine, 295 Congress Avenue, New Haven, Connecticut 06536, USA.
Abstract
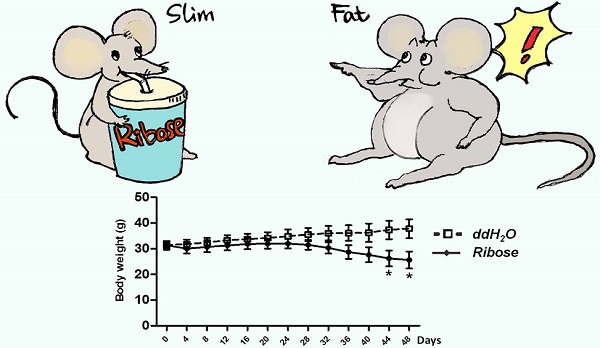
The increasing prevalence of obesity is closely related to excessive energy consumption. Clinical intervention of energy intake is an attractive strategy to fight obesity. However, the current FDA-approved weight-loss drugs all have significant side effects. Here we show that ribose upregulates gut motility and suppresses mice body weight gain. Ribokinase, which is encoded by Rbks gene, is the first enzyme for ribose metabolism in vivo. Rbks mutation resulted in ribose accumulation in the small intestine, which accelerated gut movement. Ribose oral treatment in wild type mice also enhanced bowel motility and rendered mice resistance to high fat diets. The suppressed weight gain was resulted from enhanced ingested food excretion. In addition, the effective dose of ribose didn't cause any known side effects (i.e. diarrhea and hypoglycemia). Overall, our results show that ribose can regulate gut motility and energy homeostasis in mice, and suggest that administration of ribose and its analogs could regulate gastrointestinal motility, providing a novel therapeutic approach for gastrointestinal dysfunction and weight control.
Keywords: Ribose, ribokinase, gut motility, body weight control.
