ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(8):931-943. doi:10.7150/ijbs.15447 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Protein Elicitor PevD1 Enhances Resistance to Pathogens and Promotes Growth in Arabidopsis
State Key Laboratory for Biology of Plant Diseases and Insect Pests, Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, 100081, China.
Abstract
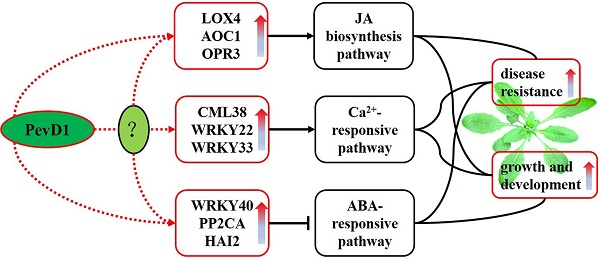
The protein elicitor PevD1, isolated from Verticillium dahlia, could enhance resistance to TMV in tobacco and Verticillium wilt in cotton. Here, the pevd1 gene was over-expressed in wild type (WT) Arabidopsis, and its biological functions were investigated. Our results showed that the transgenic lines were more resistant to Botrytis cinerea and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 than the WT line was. In transgenic plants, both the germination time and bolting time required were significantly shorter and fresh weights and plant heights were significantly higher than those in the WT line. A transcriptomics study using digital gene expression profiling (DGE) was performed in transgenic and WT Arabidopsis. One hundred and thirty-six differentially expressed genes were identified. In transgenic Arabidopsis, three critical regulators of JA biosynthesis were up-regulated and JA levels were slightly increased. Three important repressors of the ABA-responsive pathway were up-regulated, indicating that ABA signal transduction may be suppressed. One CML and two WRKY TFs involved in Ca2+-responsive pathways were up-regulated, indicating that this pathway may have been triggered. In conclusion, we show that PevD1 is involved in regulating several plant endogenous signal transduction pathways and regulatory networks to enhance resistance and promote growth and development in Arabidopsis.
Keywords: PevD1, transgene, disease resistance, growth phenotype, transcriptomics, signaling pathway.
