ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(9):1129-1139. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16319 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Selection of Reference Genes for Expression Studies of Xenobiotic Adaptation in Tetranychus urticae
1. Department of Entomology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164, USA;
2. Irrigated Agriculture Research and Extension Center, Washington State University, Prosser, WA 99350, USA.
Abstract
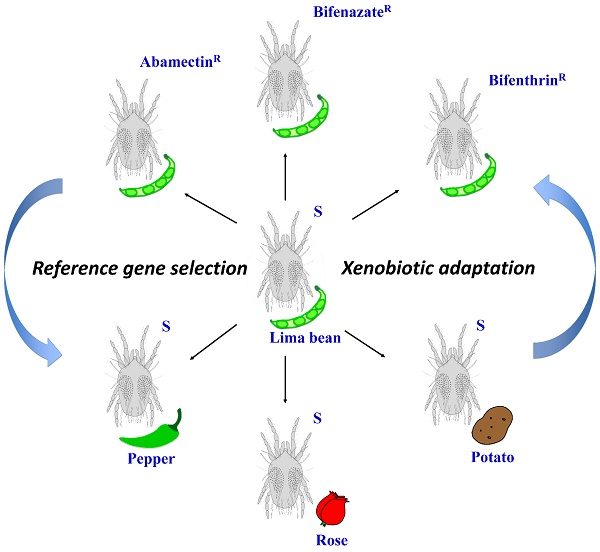
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) is an extensively used, high-throughput method to analyze transcriptional expression of genes of interest. An appropriate normalization strategy with reliable reference genes is required for calculating gene expression across diverse experimental conditions. In this study, we aim to identify the most stable reference genes for expression studies of xenobiotic adaptation in Tetranychus urticae, an extremely polyphagous herbivore causing significant yield reduction of agriculture. We chose eight commonly used housekeeping genes as candidates. The qRT-PCR expression data for these genes were evaluated from seven populations: a susceptible and three acaricide resistant populations feeding on lima beans, and three other susceptible populations which had been shifted host from lima beans to three other plant species. The stability of the candidate reference genes was then assessed using four different algorithms (comparative ΔCt method, geNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper). Additionally, we used an online web-based tool (RefFinder) to assign an overall final rank for each candidate gene. Our study found that CycA and Rp49 are best for investigating gene expression in acaricide susceptible and resistant populations. GAPDH, Rp49, and Rpl18 are best for host plant shift studies. And GAPDH and Rp49 were the most stable reference genes when investigating gene expression under changes in both experimental conditions. These results will facilitate research in revealing molecular mechanisms underlying the xenobiotic adaptation of this notorious agricultural pest.
Keywords: xenobiotics adaptation, reference gene, constitutive expression, qRT-PCR, analysis parameters.
