ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(10):1320-1328. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19462 This issue Cite
Review
Complexity Change in Cardiovascular Disease
1. Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau;
2. Department of Geriatrics, Centro Hospital Conde de Sao Januario, Macau;
3. Department of Cardiovascular Diseases, Beijing Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China;
4. State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, The 1st Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
* These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
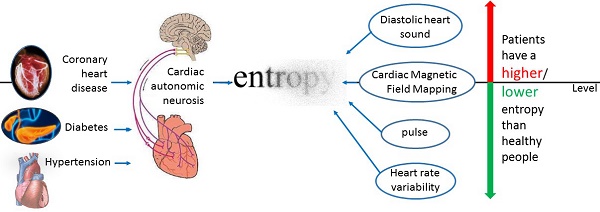
With the fast development of wearable medical device in recent years, it becomes critical to conduct research on continuously measured physiological signals. Entropy is a key metric for quantifying the irregularity and/or complexity contained in human physiological signals. In this review, we focus on exploring how entropy changes in various physiological signals in cardiovascular diseases. Our review concludes that the direction of entropy change relies on the physiological signals under investigation. For heart rate variability and pulse index, the entropy of a healthy person is higher than that of a patient with cardiovascular diseases. For diastolic period variability and diastolic heart sound, the direction of entropy change is reversed. Our conclusion should not only give valuable guidance for further research on the application of entropy in cardiovascular diseases but also provide a foundation for using entropy to analyze the irregularity and/or complexity of physiological signals measured by wearable medical device.
Keywords: entropy, physiological signal, cardiovascular disease, irregularity, complexity.
