ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(5):531-541. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23945 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PARI functions as a new transcriptional target of FOXM1 involved in gastric cancer development
1. Department of Oncology, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China;
2. Department of Hematology & Oncology, the People's Hospital of Beilun District, Beilun Branch Hospital of the First Affiliated Hospital of Medical School of Zhejiang University, Ningbo 315800, China;
3. Department of Pharmacy, Changhai Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
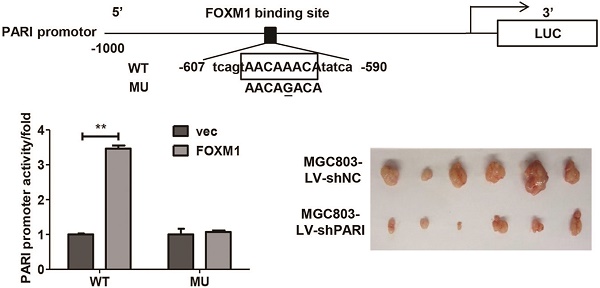
PARI, an element of the homologous recombination pathway of DNA repair,is involved in the regulation of cell cycle and carcinogenesis in pancreatic cancer. However, little is known about the function and regulatory mechanism of PARI in other cancers. In the present study, we evaluated the expression of PARI in gastric cancer (GC) by immunohistochemical analysis in a tissue microarray and characterized its functions using in vitro assays and in vivo animal models. We found higher expression of PARI protein was shown in GC tissues compared with related adjacent normal gastric mucosa tissues. Knockdown of PARI by RNA inference decreased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of GC cells in vitro, as well as reduced the xenograft tumor growth and lung metastasis formation in vivo. Quantitative real-time PCR and western blot results revealed that PARI expression was activated by a well-known oncogene FOXM1 and positively correlated with FOXM1 expression at mRNA level in 38 paired of GC samples. Luciferase reporter assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay further demonstrated that FOXM1 directly regulated PARI transcription by binding to the specific sequences of PARI promoter. In addition, PARI knockdown blocked the effect of FOXM1 on GC cell migration. Taken together, our results suggest that PARI plays potential oncogenic roles and functions as a transcriptional target and effector of FOXM1 in GC development.
Keywords: PARI, FOXM1, Gastric cancer, Proliferation, Migration
