ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(6):622-632. doi:10.7150/ijbs.24223 This issue Cite
Research Paper
miR-433 inhibits breast cancer cell growth via the MAPK signaling pathway by targeting Rap1a
Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
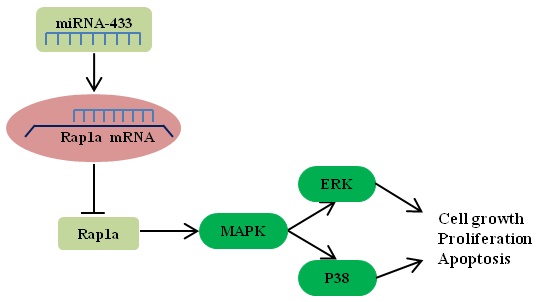
Breast cancer is one of the most lethal cancers in the world. The fight against breast cancer has also become a major task for medical workers. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are often aberrantly expressed in diverse cancers and are involved in progression and metastasis. Many studies have found that miRNAs can act as oncogenes or as tumor suppressor genes. Here, we show that miR-433 is significantly decreased in breast cancer cells. In addition, we demonstrate the effects of miR-433 on breast cancer cell apoptosis, migration and proliferation in an attempt to elucidate the mechanism of action of miR-433. Moreover, Rap1a was predicted to be a potential target of miR-433 using bioinformatic approaches, and we found that the expression of Rap1a is inversely correlated with the level of miR-433. Further studies through overexpression and knockdown of Rap1a confirmed that Rap1a, as a direct target gene of miR-433, contributes to the functions of miR-433. In addition, we found that Rap1a activates the MAPK signaling pathway, which can contribute to cell migration and proliferation and can inhibit apoptosis. Overall, these findings highlight miR-433 as a tumor suppressor gene in the regulation of the progression and metastatic potential of breast cancer and may benefit the future development of therapies targeting miR-433 in breast cancer.
Keywords: miR-433, breast cancer, Rap1a, MAPK, proliferation, apoptosis
