ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(10):1221-1231. doi:10.7150/ijbs.25488 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Simultaneously targeting DNA damage repair pathway and mTORC1/2 results in small cell lung cancer growth arrest via ER stress-induced apoptosis
1. Department of Dermatology, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, 72205
2. Department of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
3. Collaborative Innovation Center of Hematology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Abstract
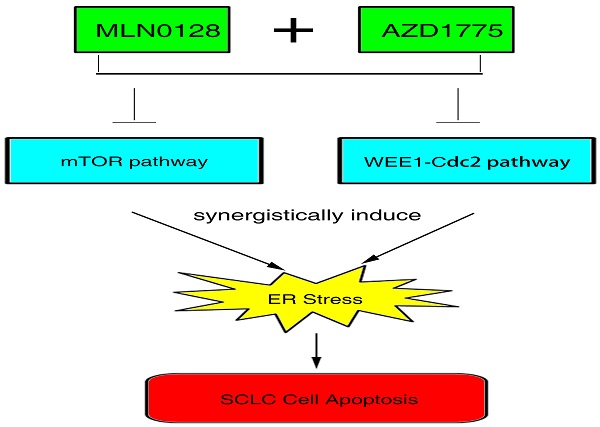
Purpose: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is highly lethal with no effective therapy. Wee1 kinase inhibitor AZD1775 (MK-1775) and mTOR kinase inhibitor MLN0128 (TAK228) are in clinical trials for relapsed SCLC and recurrent lung cancer, respectively. However, there is no preclinical data combining these two drugs in human cancers.
Methods: In this study, we set to investigate the combinatorial anti-tumor effects of AZD1775 and MLN0128 on two human SCLC cell lines H69 and H82 in vitro and in vivo.
Results: We have found that AZD1775 or MLN0128 treatment results in remarkably suppressed cell proliferation and increased cell death in vitro, what's more, the salient finding here is the potent anti-tumor effect observed in combinatorial treatment in H82 xenograft tumor. Importantly, we have first observed marked induction of ER stress and CHOP-dependent SCLC cell apoptosis in MLN0128 and AZD1775-primed cells.
Conclusion: Our study has first provided preclinical evidence that combination of AZD1775 and MLN0128 could be a novel effective therapy for advanced SCLC patients.
Keywords: Small Cell Lung Cancer, AZD1775, MLN0128, CHOP, ER Stress, Apoptosis
