ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(14):2037-2050. doi:10.7150/ijbs.28435 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hepatoprotective effects of limb ischemic post-conditioning in hepatic ischemic rat model and liver cancer patients via PI3K/ERK pathways
1. Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China;
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Texas 76502, USA;
3. Neuroscience Institute, Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Texas 76502, USA;
4. Department of Surgery, Texas A & M University Health Science Center, College of Medicine, Texas 76508, USA;
5. Department of Neurology, Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Texas 76502, USA;
6. Department of Statistics, North Dakota State University, Fargo, North Dakota 58105, USA;
7. Department of Neurology, University of Arkansas for Medical Science, Little Rock, Arkansas 72205, USA;
8. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Texas A & M University Health Science Center, College of Pharmacy, College Station, Texas 77843, USA;
9. LIVESTRONG Cancer Institutes, Dell Medical School, the University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas 78712, USA;
10. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China;
11. Department of General Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
*These authors contribute equally to this study
Abstract
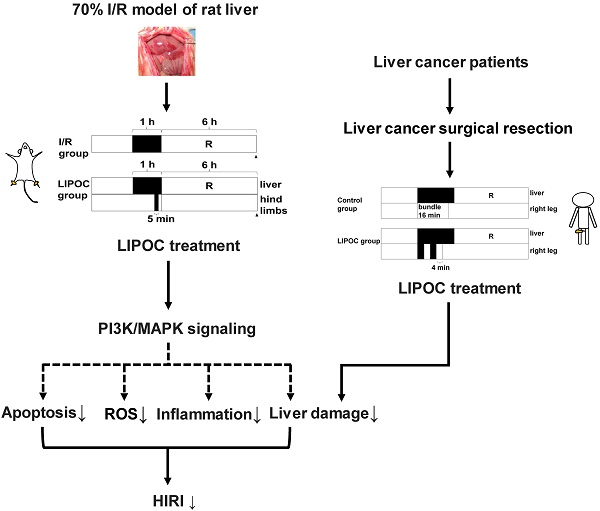
The most effective way of treating liver cancer is surgical resection, which usually requires blocking the hepatic portal circulation, and may result in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI). It is of paramount importance to control HIRI for liver cancer surgical resection. In this study, a 70% ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) model of rat liver was established, and the protective effect and mechanism of limb ischemic post-conditioning (LIPOC) on HIRI was investigated. We show that LIPOC has a protective effect on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats, which reduces the elimination of superoxide dismutase, thereby increasing oxygen free radical scavenging, decreasing lipid peroxidation, inhibiting neutrophil aggregation, as well as reducing TNFα, IL1β, and other inflammatory cytokines. In addition, LIPOC inhibited the apoptosis of hepatocytes induced by I/R injury, and decreased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Furthermore, LIPOC promoted the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. The use of PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and ERK1/2 blocker PD98059 inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2 caused by LIPOC and abolished the injury protection of liver I/R. Moreover, through 16 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma resections, we found that short-term LIPOC treatment significantly suppressed the elevated alanine aminotransferase, aspartic transaminase, and total bilirubin in the early post-operation of liver resection, and reduced reperfusion injury to the ischemic liver. In summary, our study demonstrates that LIPOC could be an effective method for HIRI in the clinical implementation of liver resection and uncovers the potential mechanism of LIPOC in the protective effects of HIRI.
Keywords: limb ischemic postconditioning (LIPOC), hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury, liver cancer, hepatectomy, reperfusion injury salvage kinase
