ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(14):2051-2064. doi:10.7150/ijbs.28576 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SRC-3 protects intestine from DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting inflammation and promoting goblet cell differentiation through enhancement of KLF4 expression
1. Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, Innovation Center for Cell Biology, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China;
3. Xiamen Medical College, Xiamen Fujian 361023,China.
4. Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA.
* These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
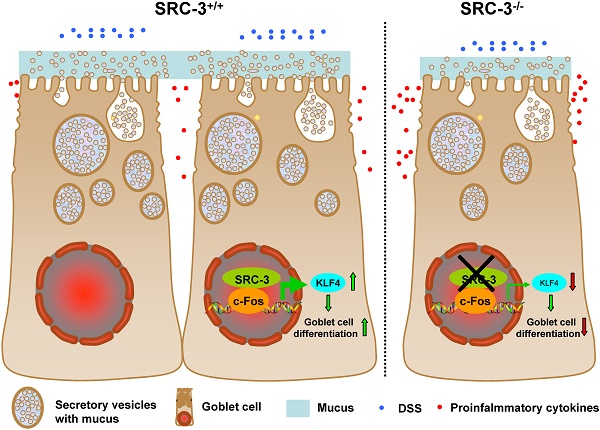
Goblet cell loss, which leads to the reduction of mucin secretion, is a hallmark of ulcerative colitis (UC). We previously reported that steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3), a transcriptional coactivator, contributes to host defense against Citrobacter rodentium by recruiting neutrophils, suggesting a role of SRC-3 in intestine homeostasis. However, the biological role of SRC-3 in UC remains unclear. Here, we showed that SRC-3-/- mice were more susceptible to dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis compared with wild-type mice after oral administration of 2% DSS dissolved in drinking water. After oral administration of 2% DSS, SRC-3-/- mice displayed higher mortality rate, significant body weight loss, and higher clinical symptom scores compared to wild-type mice. SRC-3-/- mice suffered a severe loss of mature colonic goblet cells, leading to more severe histopathology and more proinflammatory cytokine production. Mechanistically, SRC-3-/- mice exhibited a decreased expression of transcription factor KLF4 in the colons, which is responsible for colonic goblet cell differentiation and maturation. At the molecular level, SRC-3 cooperated with c-Fos to promote KLF4 expression at the transcriptional level. These results demonstrate that SRC-3 can ameliorate DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting inflammation and promoting colonic goblet cell differentiation and maturation through enhancing the expression of transcriptional factor KLF4, which is responsible for colonic goblet cell differentiation and maturation.
Keywords: SRC-3, ulcerative colitis, goblet cell
