ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(8):1618-1629. doi:10.7150/ijbs.33323 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tripartite Motif 8 Deficiency Relieves Hepatic Ischaemia/reperfusion Injury via TAK1-dependent Signalling Pathways
Department of Organ Transplantation, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430060, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work as co-first authors in this paper.
Abstract
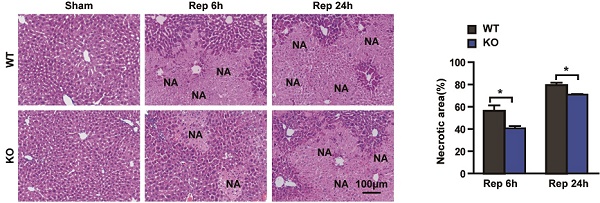
Tripartite motif (Trim) 8 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase, interacting with and ubiquitinating diverse substrates, and is closely involved in innate immunity. However, the function of Trim8 in hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury remains largely unknown. The aim of this study is to explore the role of Trim8 in hepatic I/R injury. Trim8 gene knockout mice and primary hepatocytes were used to construct hepatic I/R models. The effect of Trim8 on hepatic I/R injury was analysed via pathological and molecular analyses. The results indicated that Trim8 was significantly upregulated in liver of mice subjected to hepatic I/R injury. Trim8 knockout relieved hepatocyte injury triggered by I/R. Silencing of Trim8 expression alleviated hepatic inflammation responses and inhibited apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, our study suggests that Trim8 deficiency may elicit hepatic protective effects by inhibiting the activation of transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-p38/JNK signalling pathways. TAK1 was required for Trim8 function in hepatic I/R injury as TAK1 activation abolished Trim8 function in vitro. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that Trim8 deficiency plays a protective role in hepatic I/R injury by inhibiting the activation of TAK1-dependent signalling pathways.
Keywords: Trim8, Ischaemia/reperfusion, Inflammation, Apoptosis, Hepatology, Ubiquitination
