ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(10):2075-2086. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23802 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Deregulation of CSMD1 targeted by microRNA-10b drives gastric cancer progression through the NF-κB pathway
1. Department of Digestive Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University; the First Provincial Wenzhou Hospital of Zhejiang, Wenzhou 325000.
2. Zhejiang Cancer Institute, Institute of Cancer Research and Basic Medical Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Cancer Hospital of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou 310022, China.
3. Department of Digestive Oncology, Zhejiang Province Cancer Hospital, Zhejiang Cancer Center, Hangzhou 310022, China.
*Contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the oncogenic activity of microRNA-10b by targeting CUB and sushi multiple domains protein 1 (CSMD1) in human gastric cancer (GC) and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: The expression of CSMD1 in human GC tissues was evaluated by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), immunoblotting, and immunohistochemical analysis. The expressive abundance of microRNA-10b was detected by stem-loop RT-PCR. Molecular and cellular techniques, including lentiviral vector-mediated knockdown or overexpression, were used to elucidate the effect of microRNA-10b on the expression of CSMD1.
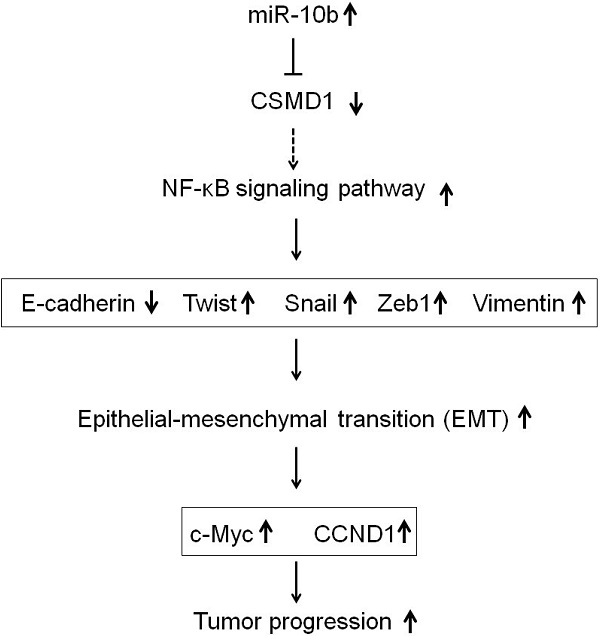
Results: CSMD1 was targeted and downregulated by microRNA-10b in human GC tissues and cells, and the down-regulated expression of CSMD1 contributed to poor survival. The knockdown of microRNA-10b expression inhibited cell proliferation in GC cells in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. The inhibition of microRNA-10b expression repressed invasion and migration of HGC27 cells and retarded GC cells metastasis to the liver in Balb/c nude mice. The up-regulated expression of microRNA-10b promoted the proliferation and metastasis of MKN74 cell in vitro. Intratumoral injection of microRNA-10b mimic also promoted the growth and metastasis of tumor xenografts in Balb/c nude mice. Mechanistically, microRNA-10b promoted the invasion and metastasis of human GC cells through inhibiting the expression of CSMD1, leading to the activation of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway that links inflammation to carcinogenesis, subsequently resulting in the upregulation of c-Myc, cyclin D1 (CCND1), and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers.
Conclusions: The findings established that microRNA-10b is an oncomiR that drives metastasis. Moreover, a set of critical tumor suppressor mechanisms was defined that microRNA-10b overcame to drive human GC progression.
Keywords: microRNA-10b, CUB and sushi multiple domains protein 1 (CSMD1), gastric carcinoma (GC), epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), Tumor metastasis.
