ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(11):1774-1784. doi:10.7150/ijbs.42197 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Histone Acetyltransferase (HAT) P300/CBP Inhibitors Induce Synthetic Lethality in PTEN-Deficient Colorectal Cancer Cells through Destabilizing AKT
Cancer Centre, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Taipa, 999078, Macau
Abstract
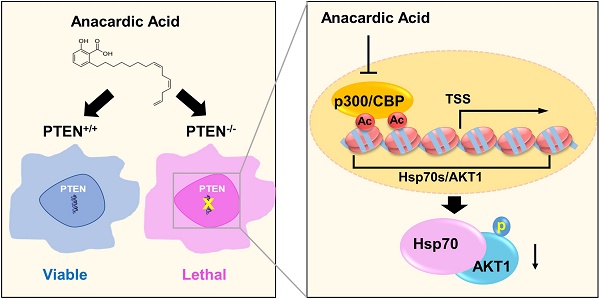
PTEN, a tumor suppressor, is found loss of function in many cancers, including colorectal cancer. To identify the synthetic lethal compounds working with PTEN deficiency, we performed a synthetic lethality drug screening with PTEN-isogenic colorectal cancer cells. From the screening, we found that PTEN-/- colorectal cancer cells were sensitive to anacardic acid, a p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitor. Anacardic acid significantly reduced the viability of PTEN-/- cells not in PTEN+/+ cells via inducing apoptosis. Inhibition of HAT activity of p300/CBP by anacardic acid reduced the acetylation of histones at the promoter region and inhibited the transcription of Hsp70 family of proteins. The down-regulation of Hsp70 family proteins led to the reduction of AKT-Hsp70 complex formation, AKT destabilization and decreased the level of phosphorylated AKT at Ser473, all of which are vital for the survival of PTEN-/- colorectal cells. The synthetic lethality effect of anacardic acid was further validated in tumor xenograft mice models, where PTEN-/- colorectal tumors showed greater sensitivity to anacardic acid treatment than PTEN+/+ tumors. These data suggest that anacardic acid induced synthetic lethality by inhibiting HAT activity of p300/CBP, thereby reducing Hsp70 transcription and destabilizing AKT in PTEN deficient colorectal cancer cells.
Keywords: PTEN, Synthetic lethality, Histone acetyltransferases, Anacardic acid, AKT, Hsp70
