10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(5):587-594. doi:10.7150/ijbs.10945 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Recognition of Cytosolic DNA Attenuates Glucose Metabolism and Induces AMPK Mediated Energy Stress Response
1. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108, China.
2. Translational Medicine Institute, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108, China.
3. Department of Bioengineering, Fujian Vocational College of Bioengineering, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350007, China
4. State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology and School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, 361102, China
5. Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02215, USA
*These two authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
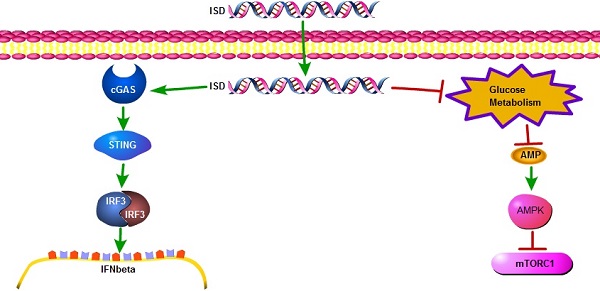
Both viral infection and DNA transfection expose single-stranded or double-stranded DNA to the cytoplasm of mammalian cells. Recognition of cytosolic DNA activates a series of cellular responses, including induction of pro-inflammatory genes such as type I interferon through the well-known cGAS-STING pathway. Here we show for the first time that intracellular administration of either single or double stranded interferon stimulating DNA (ISD), but not poly(dA) suppresses cell growth in many different cell types. Suppression of cell growth by cytosolic DNA is cGAS/STING independent and associated with inhibition of glucose metabolism, ATP depletion and subsequent cellular energy stress responses including activation of AMPK and inactivation of mTORC1. Our results suggest that in concert with but independent of innate immune response, recognition of cytosolic DNA induced cellular energy stress potentially functions as a metabolic barrier to viral replication.
Keywords: Cytosolic DNA, Glycolysis, ATP depletion, Energy stress, AMPK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact