10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(7):812-823. doi:10.7150/ijbs.15229 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Channel Involved in Atherosclerosis and Macrophage-Foam Cell Formation
1. Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
2. Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan
3. Faculty of Medicine, School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
4. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
5. Genome Research Center, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
Abstract
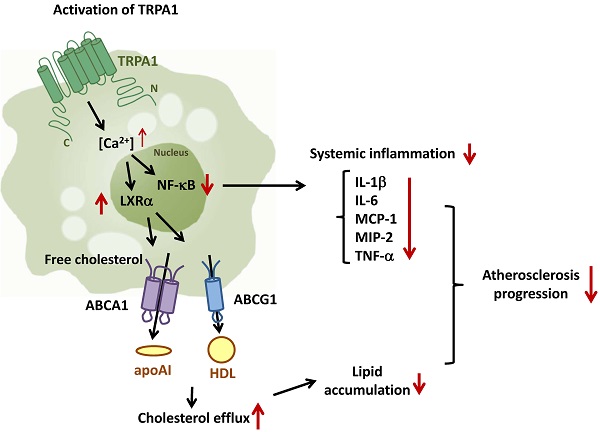
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 channel (TRPA1) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases, yet its role and the underlying mechanism in atherosclerosis remain unclear. We aimed to investigate the role of TRPA1 in atherosclerosis and foam-cell formation in vivo in mice and in vitro in mouse macrophages. Histopathology was examined by hematoxylin and eosin staining, levels of cytokines and lipid profile were evaluated by assay kits, and protein expression was determined by western blot analysis. TRPA1 expression was increased in macrophage foam cells in atherosclerotic aortas of apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE-/-) mice. Atherosclerotic lesions, hyperlipidemia and systemic inflammation were worsened with chronic administration of the TRPA1 channel antagonist HC030031 or genetic ablation of TRPA1 (TRPA1-/-) in apoE-/- mice. Treatment with allyl isothiocyanate (AITC, a TRPA1 agonist) retarded the progression of atherosclerosis in apoE-/- mice but not apoE-/-TRPA1-/- mice. Mouse macrophages showed oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) activated TRPA1 channels. OxLDL-induced lipid accumulation of macrophages was exacerbated by HC030031 or loss of function of TRPA1. Inhibition of TRPA1 activity did not alter oxLDL internalization but impaired cholesterol efflux by downregulating the ATP-binding cassette transporters. Furthermore, tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inflammatory response was attenuated in AITC-activated macrophages. TRPA1 may be a pivotal regulator in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and cholesterol metabolism of macrophage foam cells.
Keywords: TRPA1, atherosclerosis, foam cell, cholesterol efflux, inflammation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact