10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(5):604-614. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19591 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SDF-1 in Mammary Fibroblasts of Bovine with Mastitis Induces EMT and Inflammatory Response of Epithelial Cells
1. College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, Shaanxi, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Animal Biotechnology, Ministry of Agriculture, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, Shaanxi, China.
Abstract
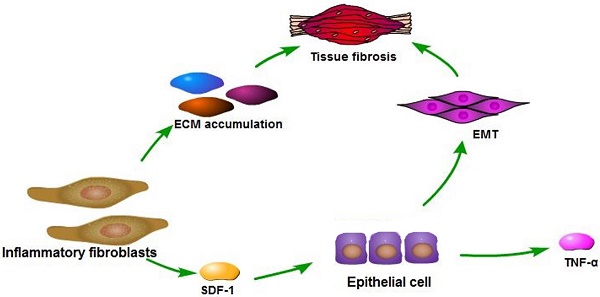
Fibroblasts constitute the majority of the stromal cells within bovine mammary gland, yet the functional contributions of these cells to mastitis and fibrosis and the mechanism are poorly understood. In this study, we demonstrate that inflammation-associated fibroblasts (INFs) extracted from bovine mammary glands with clinical mastitis had different expression pattern regarding to several extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, chemokines and cytokines compared to normal fibroblasts (NFs) from dairy cows during lactation. The INFs induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and inflammatory responses of mammary epithelial cells in a vitro co-culture model. These functional contributions of INFs to normal epithelial cells were mediated through their ability to secrete stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1). SDF-1 was highly secreted/expressed by INFs, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -treated NFs, lipoteichoic acid (LTA) -treated NFs, as well as mastitic tissue compared to their counterparts. Exogenous SDF-1 promoted EMT on epithelial cells through activating NF-κB pathway, induced inflammation response and inhibited proliferation of epithelial cells. In addition, SDF-1 was able to induce mastitis and slight fibrosis of mouse mammary gland, which was attenuated by a specific inhibitor of the receptor of SDF-1. Our findings indicate that stromal fibroblasts within mammary glands with mastitis contribute to EMT and inflammatory responses of epithelial cells through the secretion of SDF-1, which could result in the inflammation spread and fibrosis within mammary gland.
Keywords: Stromal cell-derived factor 1, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, fibroblasts, epithelial cells, bovine mastitis.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact