10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(7):799-806. doi:10.7150/ijbs.25928 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A dual-specific IGF-I/II human engineered antibody domain inhibits IGF signaling in breast cancer cells
1. Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Macau, China.
2. Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, California, USA.
3. National Engineering Laboratory for AIDS Vaccine, School of Life Science, Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China;
4. Department of Biology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Cell Microenvironment and Disease Research, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Cell Microenvironment, SUSTech-HKU joint laboratories for matrix biology and diseases, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
5. Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangdong, China.
6. Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute-Frederick, National Institutes of Health, Maryland, USA.
7. Center for Antibody Therapeutics, University of Pittsburgh Medical School, Pennsylvania, USA.
#equal contribution.
Abstract
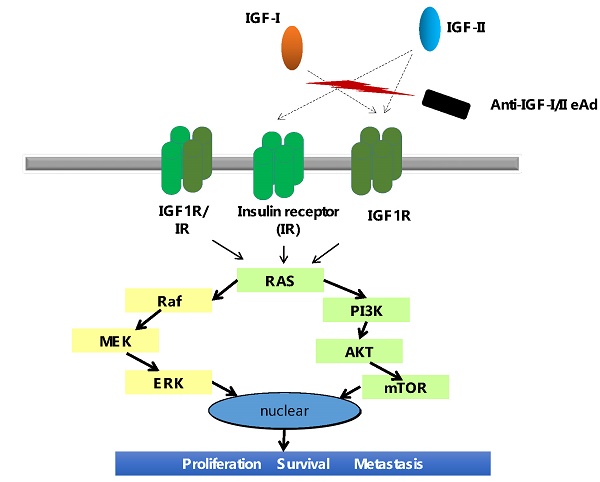
The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF-I and IGF-II, are essential for regulating cell growth, differentiation and metastasis of a broad range of malignancies. The IGF-I/II actions are mediated through the IGF receptor type 1 (IGF-1R) and the insulin receptor (IR), which are overexpressed in multiple types of tumors. Here, we have firstly identified a human engineered antibody domain (eAd) from a phage-displayed VH library. The eAd suppressed the signal transduction of IGF-1R mediated by exogenous IGF-I or IGF-II in breast cancer cell lines through neutralizing both IGF-I and IGF-II. It also significantly inhibited the growth of breast cancer cells. Therefore, the anti-IGF-I/II eAd offers an alternative approach to target both the IGF-1R signaling pathways through the inhibition of IGF-I/II.
Keywords: Insulin-like growth factor, Yeast display, Affinity maturation, eAd

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact