10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(14):1935-1949. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27315 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A chemosensory protein MsepCSP5 involved in chemoreception of oriental armyworm Mythimna separata
1. College of Plant Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
2. College of Resources and Environment, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
3. Department of Plant Protection, Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Banha, Qalyubia 13736, Egypt
4. College of Informatics, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
Abstract
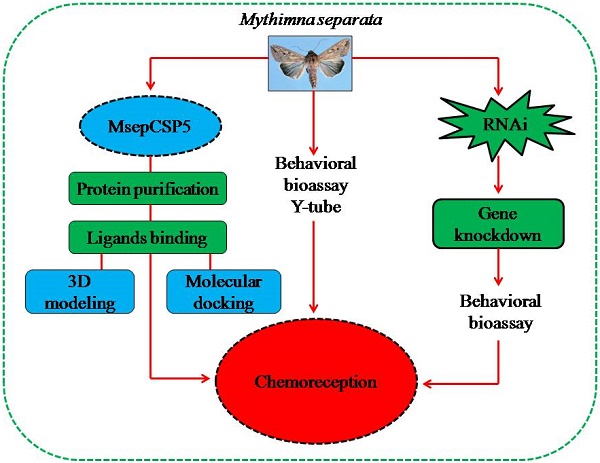
Chemosensory proteins (CSPs) have been suggested to perform several functions in insects, including chemoreception. To find out whether MsepCSP5 identified from Mythimna separata shows potential physiological functions in olfaction, gene expression profiles, ligand-binding experiments, molecular docking, RNA interference, and behavioral test were performed. Results showed that MsepCSP5 was highly expressed in female antennae. MsepCSP5 showed high binding affinities to a wide range of host-related semiochemicals, and displayed that 26 out of 35 candidate volatiles were highly bound (Ki < 10 µM) at pH 5.0 rather than pH 7.4. The binding sites of MsepCSP5 to candidate volatiles were well predicted by three-dimensional structure modeling and molecular docking experiments. Pursuing further, biological activities of M. separata to highly bound compounds elicited strong behavioral responses, such as alcoholic compounds displayed strong attractiveness whereas terpenes showed repellency to M. separata. The transcript expression level of MsepCSP5 gene significantly decreased after injecting target dsRNAs, and resulted in non-significant preference responses of M. separata to semiochemicals, such as 3-pentanol and 1-octene-3-ol. In conclusion, MsepCSP5 may involve in semiochemical reception of M. separata.
Keywords: chemosensory proteins, expression patterns, binding characteristics, behavioral response

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact