ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(14):1950-1959. doi:10.7150/ijbs.28260 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Prediction of CircRNA-Disease Associations Using KATZ Model Based on Heterogeneous Networks
1. School of Computer Science, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an 710119, China
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering and Division of Biomedical Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
Abstract
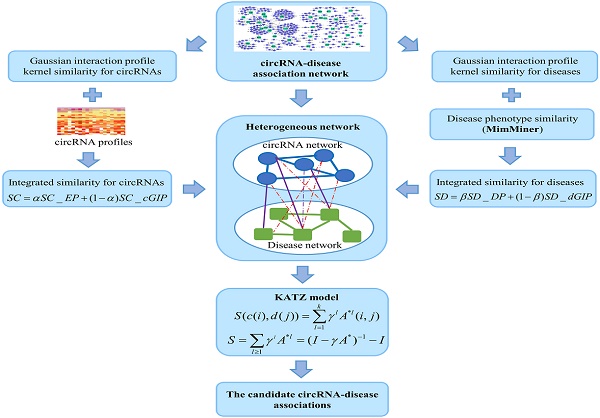
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a large group of endogenous non-coding RNAs which are key members of gene regulatory processes. Those circRNAs in human paly significant roles in health and diseases. Owing to the characteristics of their universality, specificity and stability, circRNAs are becoming an ideal class of biomarkers for disease diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Identification of the relationships between circRNAs and diseases can help understand the complex disease mechanism. However, traditional experiments are costly and time-consuming, and little computational models have been developed to predict novel circRNA-disease associations. In this study, a heterogeneous network was constructed by employing the circRNA expression profiles, disease phenotype similarity and Gaussian interaction profile kernel similarity. Then, we developed a computational model of KATZ measures for human circRNA-disease association prediction (KATZHCDA). The leave-one-out cross validation (LOOCV) and 5-fold cross validation were implemented to investigate the effects of these four types of similarity measures. As a result, KATZHCDA model yields the AUCs of 0.8469 and 0.7936+/-0.0065 in LOOCV and 5-fold cross validation, respectively. Furthermore, we analyze the candidate association between hsa_circ_0006054 and colorectal cancer, and results showed that hsa_circ_0006054 may function as miRNA sponge in the carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. Overall, it is anticipated that our proposed model could become an effective resource for clinical experimental guidance.
Keywords: CircRNA-disease association, similarity measure, KATZ model
