ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(14):2595-2611. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45886 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Chidamide increases the sensitivity of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer to Crizotinib by decreasing c-MET mRNA methylation
Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education/Beijing), Division of Etiology, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Fu-Cheng-Lu #52, Haidian District, Beijing, 100142, China.
Abstract
Introduction: Crizotinib is a kinase inhibitor targeting c-MET/ALK/ROS1 used as the first-line chemical for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with ALK mutations. Although c-MET is frequently overexpressed in 35-72% of NSCLC, most NSCLCs are primarily resistant to crizotinib treatment.
Method: A set of NSCLC cell lines were used to test the effect of chidamide on the primary crizotinib resistance in vitro and in vivo. Relationships between the synergistic effect of chidamide and c-MET expression and RNA methylation were systemically studied with a battery of molecular biological assays.
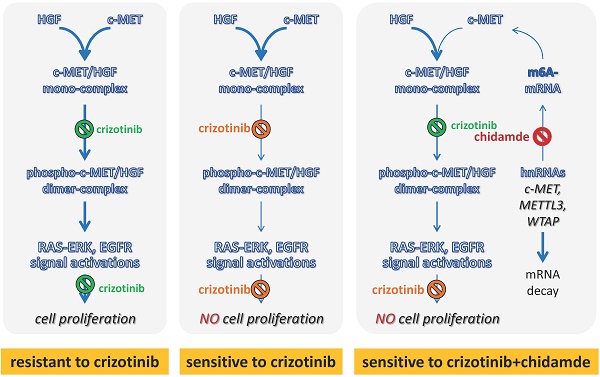
Results: We found for the first time that chidamide could sensitize the effect of crizotinib in a set of ALK mutation-free NSCLC cell lines, especially those with high levels of c-MET expression. Notably, chidamide could not increase the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to crizotinib cultured in serum-free medium without hepatocyte growth factor (HGF; a c-MET ligand). In contrast, the addition of HGF into the serum-/HGF-free medium could restore the synergistic effect of chidamide. Moreover, the synergistic effect of chidamide could also be abolished either by treatment with c-MET antibody or siRNA-knockdown of c-MET expression. While cells with low or no c-MET expression were primarily resistant to chidamide-crizotinib cotreatment, enforced c-MET overexpression could increase the sensitivity of these cells to chidamide-crizotinib cotreatment. Furthermore, chidamide could decrease c-MET expression by inhibiting mRNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification through the downregulation of METTL3 and WTAP expression. Chidamide-crizotinib cotreatment significantly suppressed the activity of c-MET downstream molecules.
Conclusion: Chidamide downregulated c-MET expression by decreasing its mRNA m6A methylation, subsequently increasing the crizotinib sensitivity of NSCLC cells in a c-MET-/HGF-dependent manner.
Keywords: chidamide, crizotinib, c-MET, non-small cell lung cancer, drug resistance
