10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(11):3293-3306. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84067 This issue Cite
Research Paper
FOXM1-regulated ZIC2 promotes the malignant phenotype of renal clear cell carcinoma by activating UBE2C/mTOR signaling pathway
1. Department of Urology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, P.R. China.
2. Graduate School of Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, P.R. China.
3. Department of Urology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, P.R. China.
4. Department of Urology, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, P.R. China.
* These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: As a transcription factor, Zic family member 2 (ZIC2) has been involved in more and more studies of tumorigenesis, which has been proved by our research team to be an effective prognostic marker for Pan-cancer. However, the prognosis, tumor promoting effect and regulatory mechanism of ZIC2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) are still unknown.
Methods: The potential clinical significance of ZIC2 was evaluated by bioinformatics analysis using data from TCGA, GEO, and ArrayExpress data sets. WB and IHC were used to detect ZIC2 expression in tumors and adjacent tissues. CCK-8, EdU, colony formation, cell cycle, wound healing, transwell, subcutaneous xenograft, and lung metastasis models were used to detect the biological function of ZIC2. The regulatory mechanism of ZIC2 was confirmed by data of RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, MS-PCR, Chip-PCR, and luciferase reporter experiments.
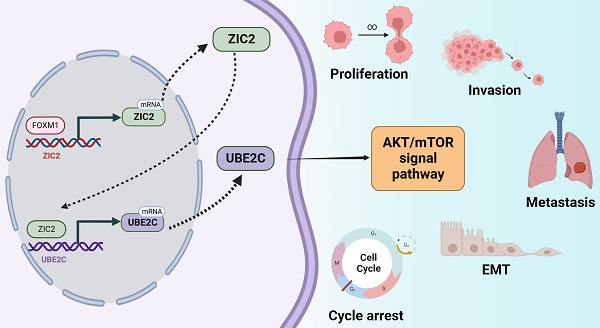
Results: ZIC2 was markedly upregulated and correlated with poor clinicopathological features in ccRCC. Knockdown of ZIC2 resulted in reduced cell proliferation, invasion, migration, induction of G2/M phase arrest, and reduced tumor formation and lung metastasis in nude mice. The opposite was observed after overexpression. Mechanistically, the high expression of ZIC2 is regulated by hypomethylation and high H3K4Me3 in the promoter region, as well as positive transcriptional regulation by FOXM1. And then, ZIC2 transcriptase-positively regulates UBE2C and activates AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to promote tumor malignant progression.
Conclusion: This study reveals that FOXM1-ZIC2-UBE2C-mTOR signaling axis promotes the progression of ccRCC, which can be used as a prognostic indicator and potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, ZIC2, FOXM1, UBE2C, mTOR

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact