10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(11):3483-3498. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84331 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SDC2 Stabilization by USP14 Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression through Co-option of PDK1
1. Department of Gastric Surgery, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer, Shanghai 200032, China.
2. Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Animal Embryo Engineering and Molecular Breeding of Hubei province, Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, Hubei Academy of Agricultural Science, Wuhan 430064, China.
4. Department of Pathology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 200032, China.
5. MOE Key Laboratory of Metabolism and Molecular Medicine and Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of School of Basic Medical Sciences, and Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai Medical College of Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
*Li You, Yi Dou and Yu Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
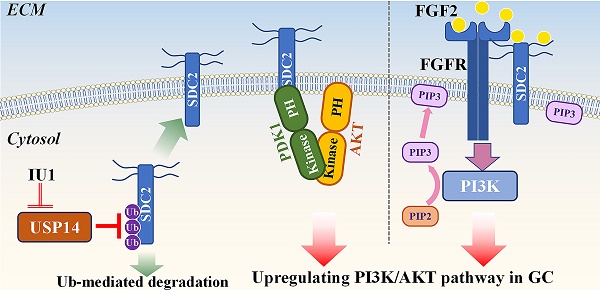
Gastric cancer (GC) is a common malignancy and remains the fourth-leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Oncogenic potential of SDC2 has been implicated in multiple types of cancers, yet its role and underlying molecular mechanisms in GC remain unknown. Here, we found that SDC2 was highly expressed in GC and its upregulation correlated with poor prognosis in GC patients. Depletion of SDC2 significantly suppressed the growth and invasive capability of GC cells, while overexpressing SDC2 exerts opposite effects. Combined bioinformatics and experimental analyses substantiated that overexpression of SDC2 activated the AKT signaling pathway in GC, mechanistically through the interaction between SDC2 and PDK1-PH domain, thereby facilitating PDK1 membrane translocation to promote AKT activation. Moreover, SDC2 could also function as a co-receptor for FGF2 and was profoundly involved in the FGF2-AKT signaling axis in GC. Lastly, we revealed a mechanism on the USP14-mediated stabilization of SDC2 that is likely to contribute to SDC2 upregulation in GC tissues. Furthermore, we showed that IU1, a potent USP14 inhibitor, decreased the abundance of SDC2 in GC cells. Our findings indicate that SDC2 functions as a novel GC oncogene and has potential utility as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for GC.
Keywords: Gastric cancer, SDC2, PDK1, FGF2, USP14.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact