ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(11):3544-3557. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82566 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MDM2 inhibition is synthetic lethal with PTEN loss in colorectal cancer cells via the p53-dependent mechanism
1. Cancer Centre, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Avenida da Universidade, Taipa, Macau SAR, China.
2. MOE Frontiers Science Centre for Precision Oncology, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau SAR, China.
Abstract
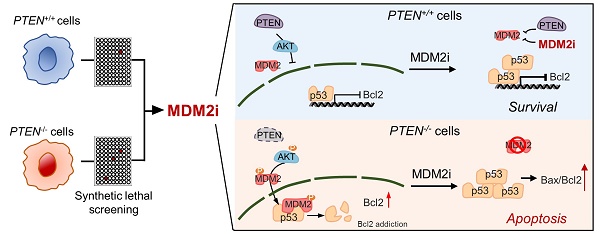
Colorectal cancer (CRC) driven by PTEN deficiency exhibits high risk of metastasis, advancement of tumor stages and chemotherapy resistance, where no effective therapy has been developed. In this study, we performed a synthetic lethal drug screening in CRC and found that PTEN-deficient CRC cells are highly vulnerable to MDM2 inhibition. MDM2 inhibitor treatment or its silencing selectively inhibited the growth of PTEN-deficient CRC in vitro and in mice models. Mechanistically, PTEN loss increased the level of active AKT and subsequently increased MDM2 phosphorylation, thereby limiting the p53 functions in PTEN-/- CRC cells. MDM2 inhibition in turn activated p53 in CRC, particularly in PTEN-/- CRC cells. The synthetic lethal effect of MDM2 inhibitor was largely dependent on p53, because p53 silenced cells or cells lacking p53 failed to exhibit synthetic lethality in PTEN-deficient cells. We further showed that MDM2 inhibition led to the p53-dependent reversal of Bcl2-Bax ratio, which contributed to mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death in PTEN-deficient CRC. This study suggests that pharmacological targeting of MDM2 could be a potential therapeutic strategy for PTEN-deficient CRC.
Keywords: PTEN, colorectal cancer, MDM2, p53, synthetic lethality
