10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(12):3661-3677. doi:10.7150/ijbs.83432 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A novel mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction after chronic kidney disease induced by retinol through JAK/STAT pathway
1. Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200000, China.
2. National Clinical Research for Interventional Medicine, Shanghai, 200000, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Viral Heart Diseases, National Health Commission, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Shanghai, 200000, China.
4. Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200000, China.
5. Department of Cardiology, Taiyuan Central Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi, 030000, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
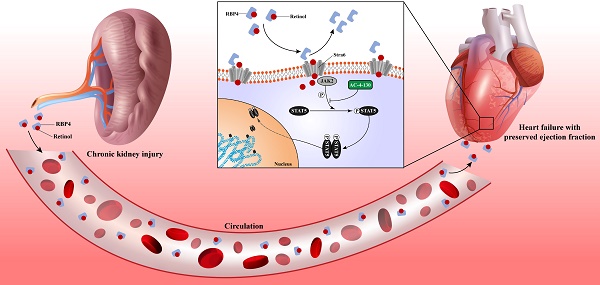
Heart failure is the leading cardiovascular comorbidity in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. Among the types of heart failure according to ejection fraction, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is the most common type of heart failure in CKD patients. However, the specific animal model of HFpEF afer CKD is currently missing. In this study, we determined the heart failure characteristics and dynamic progression in CKD mice. Based on these features, we established the practical HFpEF after CKD mouse model using 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy and retinol administration. Active apoptosis, impaired calcium handling, an imbalance between eNOS and oxidative stress and engaged endoplasmic reticulum stress were observed in our model. RNSseq revealed distinct gene expression patterns between HFpEF after CKD and metabolic induced-HFpEF. Furthermore, we revealed the potential mechanism of the pro-HFpEF effect of retinol. Serum accumulation of retinol in CKD prompts myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis by activating JAK2 and phosphorylating STAT5. Finally, using small molecule inhibitor AC-4-130, we found STAT5 phosphorylation inhibitor may be a potential intervention target for HFpEF after CKD. In conclusion, we provide a novel animal model and a potential drug target for HFpEF intervention in CKD.
Keywords: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, chronic kidney disease, retinol, animal model, JAK/STAT

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact