10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(12):3831-3868. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85753 This issue Cite
Review
Unraveling the Complexity of Regulated Cell Death in Esophageal Cancer: from Underlying Mechanisms to Targeted Therapeutics
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.
3. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Medical School, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, 518000, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
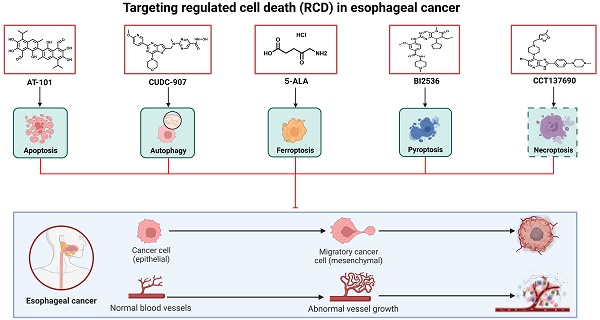
Esophageal cancer (EC) is the sixth most common and the seventh most deadly malignancy of the digestive tract, representing a major global health challenge. Despite the availability of multimodal therapeutic strategies, the existing EC treatments continue to yield unsatisfactory results due to their limited efficacy and severe side effects. Recently, knowledge of the subroutines and molecular mechanisms of regulated cell death (RCD) has progressed rapidly, enhancing the understanding of key pathways related to the occurrence, progression, and treatment of many types of tumors, including EC. In this context, the use of small-molecule compounds to target such RCD subroutines has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with EC. Thus, in this review, we firstly discussed the risk factors and prevention of EC. We then outlined the established treatment regimens for patients with EC. Furthermore, we not only briefly summarized the mechanisms of five best studied subroutines of RCD related to EC, including apoptosis, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis and autophagy, but also outlined the recent advances in the development of small-molecule compounds and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) targeting the abovementioned RCD subroutines, which may serve as a new therapeutic strategy for patients with EC in the future.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer, Cancer therapy, Regulated cell death, Small-molecule compounds, Long non-coding RNA

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact