Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(12):3892-3907. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86636 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Syntaxin-6 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and alters its sensitivity to chemotherapies by activating the USF2/LC3B axis
1. State Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Cancer, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China.
2. Department of Oncology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200080, China.
3. School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Tech University, Shanghai 201210, China.
4. Qi Dong Liver Cancer Institute, Qi Dong 226200, China.
Abstract
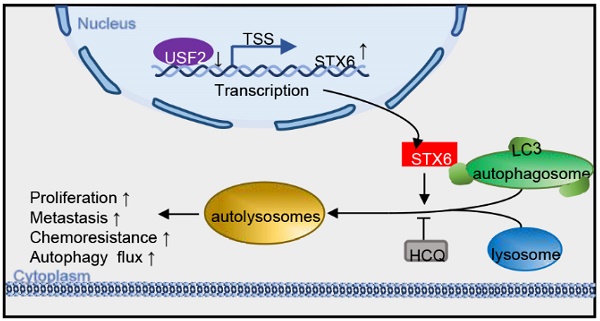
Syntaxin-6 (STX6), a protein of the syntaxin family, is located in the trans-Golgi network and is involved in a variety of intracellular membrane transport events. STX6 is overexpressed in different human malignant tumors. However, little is known about its exact function and molecular mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we found that the expression of STX6 was significantly increased in HCC tissues and was associated with poor survival. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments showed that STX6 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, STX6 was negatively regulated by the upstream stimulatory factor 2 (USF2). In addition, STX6 facilitates the association of autophagosomes with lysosomes. Importantly, we demonstrated that STX6 overexpression, despite enhanced resistance to lenvatinib, sensitizes HCC cells to the autophagy activator rapamycin. This study revealed that, under the control of USF2, STX6 accelerates the degradation of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta (LC3) by promoting autophagic flux, ultimately promoting HCC progression. Collectively, we suggest that the USF2-STX6-LC3B axis is a potential therapeutic target in liver cancer.
Keywords: STX6, hepatocellular carcinoma, metastasis, proliferation, drug resistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact