ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(13):4082-4102. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85028 This issue Cite
Research Paper
N-Acetylcysteine overcomes epalrestat-mediated increase of toxic 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and potentiates the anti-arthritic effect of epalrestat in AIA model
1. Dr. Neher's Biophysics Laboratory for Innovative Drug Discovery, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, China.
2. Faculty of Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, China.
3. Centro Hospitalar Conde de São Januário, Macau, China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
5. Macau Medical Science and Technology Research Association, Macau, China.
Abstract
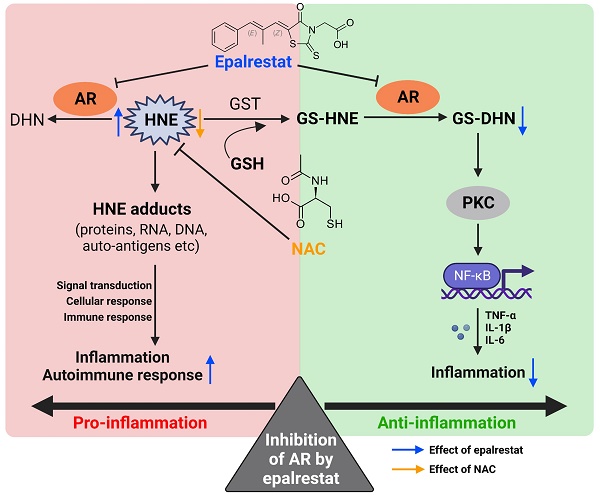
Epalrestat, an aldose reductase inhibitor (ARI), has been clinically adopted in treating diabetic neuropathy in China and Japan. Apart from the involvement in diabetic complications, AR has been implicated in inflammation. Here, we seek to investigate the feasibility of clinically approved ARI, epalrestat, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The mRNA level of AR was markedly upregulated in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of RA patients when compared to those of healthy donors. Besides, the disease activity of RA patients is positively correlated with AR expression. Epalrestat significantly suppressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the human RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RAFLSs). Unexpectedly, epalrestat treatment alone markedly exaggerated the disease severity in adjuvant induced arthritic (AIA) rats with elevated Th17 cell proportion and increased inflammatory markers, probably resulting from the increased levels of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) and malondialdehyde (MDA). Interestingly, the combined treatment of epalrestat with N-Acetylcysteine (NAC), an anti-oxidant, to AIA rats dramatically suppressed the production of 4-HNE, MDA and inflammatory cytokines, and significantly improved the arthritic condition.
Taken together, the anti-arthritic effect of epalrestat was diminished or even overridden by the excessive accumulation of toxic 4-HNE or other reactive aldehydes in AIA rats due to AR inhibition. Co-treatment with NAC significantly reversed epalrestat-induced upregulation of 4-HNE level and potentiated the anti-arthritic effect of epalrestat, suggesting that the combined therapy of epalrestat with NAC may sever as a potential approach in treating RA. Importantly, it could be regarded as a safe intervention for RA patients who need epalrestat for the treatment of diabetic complications.
Keywords: Epalrestat, AR inhibitor, Rheumatoid arthritis, 4-hydroxynonenal, N-acetylcysteine
