ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(13):4242-4258. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85739 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Exploration of diagnostic biomarkers, microenvironment characteristics, and ursolic acid's therapeutic effect for benign prostate hyperplasia
1. Department of Urology, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.
2. Department of Emergency, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
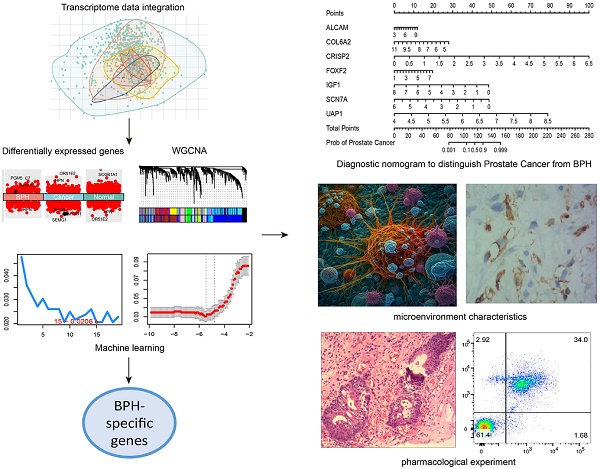
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and early-stage prostate cancer (PC) have similar symptoms, making it challenging to differentially diagnose these two conditions. The study used Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis, as well as two machine learning strategies to identify BPH-specific biomarkers based on an integrated transcriptome data from 922 samples. Eight prognostic genes (ALCAM, COL6A2, CRISP2, FOXF2, IGF1, PTN, SCN7A, and UAP1) were identified to be BPH-specific biomarkers with high accuracy and specificity. Moreover, we constructed a seven-gene diagnostic classifier to distinguish BPH from PC. The infiltrations of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and neutrophil cells showed distinct differences between BPH and non-BPH groups. Additionally, ursolic acid can reverse transcriptional features associated with the occurrence and progression of BPH. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments have confirmed that it induces apoptosis of BPH cells and inhibits cell proliferation by promoting cell cycle S-phase arrest. The diagnostic biomarkers, microenvironment characteristics, and therapeutic effect of ursolic acid explored in this study offer new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for BPH.
Keywords: diagnostic biomarkers, microenvironment characteristics, machine learning, nomogram, ursolic acid, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer
