10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(15):4709-4725. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82765 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Loss of DDRGK1 impairs IRE1α UFMylation in spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
1. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Implants, Department of Orthopedics, Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Institute of Precision Medicine, The Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
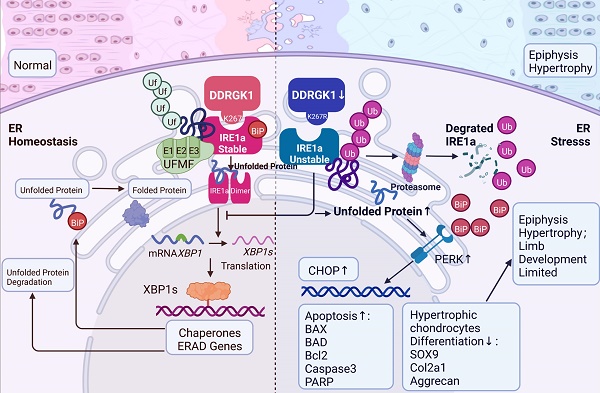
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SEMD) is a rare disease in which cartilage growth is disrupted, and the DDRGK1 mutation is one of the causative genes. In our study, we established Ddrgk1fl/fl, Col2a1-ERT Cre mice, which showed a thickened hypertrophic zone (HZ) in the growth plate, simulating the previous reported SEMD pathology in vivo. Instead of the classical modulation mechanism towards SOX9, our further mechanism study found that DDRGK1 stabilizes the stress sensor endoplasmic reticulum-to-nucleus signaling 1 (IRE1α) to maintain endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homoeostasis. The loss of DDRGK1 decreased the UFMylation and subsequently led to increased ubiquitylation-mediated IRE1α degradation, causing ER dysfunction and activating the PERK/CHOP/Caspase3 apoptosis pathway. Further DDRGK1 K268R-mutant mice revealed the importance of K268 UFMylation site in IRE1α degradation and subsequent ER dysfunction. In conclusion, DDRGK1 stabilizes IRE1α to ameliorate ER stress and following apoptosis in chondrocytes, which finally promote the normal chondrogenesis.
Keywords: spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, DDRGK1, IRE1α, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact