10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(15):4898-4914. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84970 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inonotus obliquus upregulates muscle regeneration and augments function through muscle oxidative metabolism
1. Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon 16419, Republic of Korea.
2. Research Institute of Aging Related Disease, AniMusCure Inc., Suwon 16419, Republic of Korea.
3. School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 16419, Republic of Korea.
4. Department of Chemistry, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN 37235, United States.
5. Department of Biological Sciences, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN 37235, United States.
6. Drug Information Research Institute, Muscle Physiome Research Center, College of Pharmacy, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul 04310, Republic of Korea.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
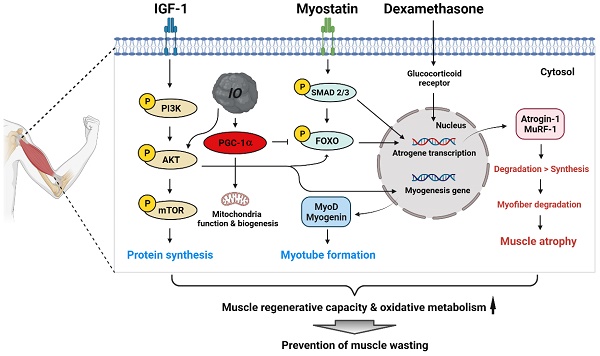
Skeletal muscle wasting related to aging or pathological conditions is critically associated with the increased incidence and prevalence of secondary diseases including cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndromes, and chronic inflammations. Much effort is made to develop agents to enhance muscle metabolism and function. Inonotus obliquus (I. obliquus; IO) is a mushroom popularly called chaga and has been widely employed as a folk medicine for inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer in Eastern Europe and Asia. However, its effect on muscle health has not been explored. Here, we aimed to investigate the beneficial effect of IO extract in muscle regeneration and metabolism. The treatment of IO in C2C12 myoblasts led to increased myogenic differentiation and alleviation of dexamethasone-induced myotube atrophy. Network pharmacological analysis using the identified specific chemical constituents of IO extracts predicted protein kinase B (AKT)-dependent mechanisms to promote myogenesis and muscle regeneration. Consistently, IO treatment resulted in the activation of AKT, which suppressed muscle-specific ubiquitin E3 ligases induced by dexamethasone. IO treatment in mice improved the regeneration of cardiotoxin-injured muscles accompanied by elevated proliferation and differentiation of muscle stem cells. Furthermore, it elevated the mitochondrial content and muscle oxidative metabolism accompanied by the induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator α (PGC-1α). Our current data suggest that IO is a promising natural agent in enhancing muscle regenerative capacity and oxidative metabolism thereby preventing muscle wasting.
Keywords: Inonotus obliquus, PGC-1α, Muscle regeneration, Muscle atrophy, Muscle oxidative metabolism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact