10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(16):5187-5203. doi:10.7150/ijbs.87977 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A novel lncRNA-mediated epigenetic regulatory mechanism in periodontitis
1. Division of Oral Biology, Tufts University School of Dental Medicine, 136 Harrison Ave, M&V Building Room 830, Boston, MA 02111, United States.
2. Department of Periodontology, Tufts University School of Dental Medicine, Boston, MA, 02211, United States.
3. State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, Sichuan, China.
4. Department of Immunology, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, United States.
5. Data Intensive Studies Center, Tufts University, Medford, MA, United States.
6. Clinical and Translational Research, Oral Medicine, Infection, and Immunity, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Forsyth Institute, Boston, MA, United States.
7. Department of Genetics, Molecular and Cell Biology, Tufts University School of Medicine, Tufts School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences, 136 Harrison Ave, M&V Room 811, Boston, MA 02111, United States.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
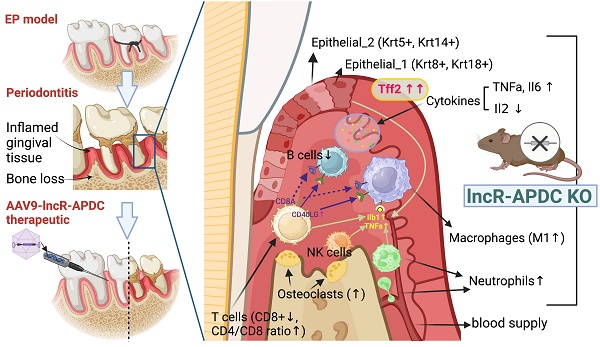
Periodontitis is a highly prevalent chronic inflammatory disease with an exaggerated host immune response, resulting in periodontal tissue destruction and potential tooth loss. The long non-coding RNA, LncR-ANRIL, located on human chromosome 9p21, is recognized as a genetic risk factor for various conditions, including atherosclerosis, periodontitis, diabetes, and cancer. LncR-APDC is an ortholog of ANRIL located on mouse genome chr4. This study aims to comprehend the regulatory role of lncR-APDC in periodontitis progression. Our experimental findings, obtained from lncR-APDC gene knockout (KO) mice with induced experimental periodontitis (EP), revealed exacerbated bone loss and disrupted pro-inflammatory cytokine regulation. Downregulation of osteogenic differentiation occurred in bone marrow stem cells harvested from lncR-APDC-KO mice. Furthermore, single-cell RNA sequencing of periodontitis gingival tissue revealed alterations in the proportion and function of immune cells, including T and B cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, due to lncR-APDC silencing. Our findings also unveiled a previously unidentified epithelial cell subset that is distinctively presenting in the lncR-APDC-KO group. This epithelial subset, characterized by the positive expression of Krt8 and Krt18, engages in interactions with immune cells through a variety of ligand-receptor pairs. The expression of Tff2, now recognized for its role in chronic inflammatory conditions, exhibited a notable increase across various tissue and cell types in lncR-APDC deficient mice. Additionally, our investigation revealed the potential for a direct binding interaction between lncR-APDC and Tff2. Intra-gingival administration of AAV9-lncR-APDC was shown to have therapeutic effects in the EP model. In conclusion, our results suggest that lncR-APDC plays a critical role in the progression of periodontal disease and holds therapeutic potential for periodontitis. Furthermore, the presence of the distinctive epithelial subpopulation and significantly elevated Tff2 levels in the lncR-APDC-silenced EP model offer new perspectives on the epigenetic regulation of periodontitis pathogenesis.
Keywords: periodontitis, long-noncoding RNA, single-cell RNA sequencing, immune response, bone loss

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact