ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(16):5245-5256. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86404 This issue Cite
Review
Roles of Protein Post-Translational Modifications During Adipocyte Senescence
1. Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Medical Science, Brain Korea 21 Project, Institute of Genetic Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, 03722, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Life Science, College of Natural Science, Ewha Womans University, 52 Ewhayeodae-Gil, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, 03760, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
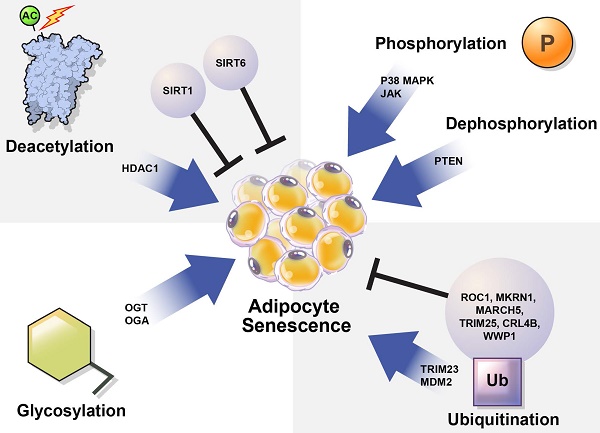
Adipocytes are adipose tissues that supply energy to the body through lipids. The two main types of adipocytes comprise white adipocytes (WAT) that store energy, and brown adipocytes (BAT), which generate heat by burning stored fat (thermogenesis). Emerging evidence indicates that dysregulated adipocyte senescence may disrupt metabolic homeostasis, leading to various diseases and aging. Adipocytes undergo senescence via irreversible cell-cycle arrest in response to DNA damage, oxidative stress, telomere dysfunction, or adipocyte over-expansion upon chronic lipid accumulation. The amount of detectable BAT decreases with age. Activation of cell cycle regulators and dysregulation of adipogenesis-regulating factors may constitute a molecular mechanism that accelerates adipocyte senescence. To better understand the regulation of adipocyte senescence, the effects of post-translational modifications (PTMs), is essential for clarifying the activity and stability of these proteins. PTMs are covalent enzymatic protein modifications introduced following protein biosynthesis, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, or glycosylation. Determining the contribution of PTMs to adipocyte senescence may identify new therapeutic targets for the regulation of adipocyte senescence. In this review, we discuss a conceptual case in which PTMs regulate adipocyte senescence and explain the mechanisms underlying protein regulation, which may lead to the development of effective strategies to combat metabolic diseases.
Keywords: Adipocyte, Senescence, Post-translational modification, Metabolic disease, Metabolic homeostasis
