ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):486-501. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86303 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Selectively targeting BCL6 using a small molecule inhibitor is a potential therapeutic strategy for ovarian cancer
1. East China Normal University, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, Institute of Biomedical Sciences and School of Life Sciences, 500 Dong Chuan Rd, Shanghai 200241, China.
2. The Jointed National Laboratory of Antibody Drug Engineering, Henan University, Kaifeng, 475004, China.
3. Department of Gynecology, The Second People's Hospital of Wuhu, Wuhu, Anhui 241000, China.
4. Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, 201203, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
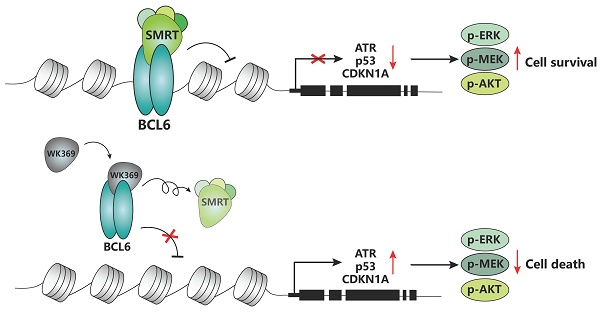
Ovarian cancer is one of the tumors with the highest fatality rate among gynecological tumors. The current 5-year survival rate of ovarian cancer is <35%. Therefore, more novel alternative strategies and drugs are needed to treat ovarian cancer. The transcription factor B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) is critically associated with poor prognosis and cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer treatment. Therefore, BCL6 may be an attractive therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. However, the role of targeting BCL6 in ovarian cancer remains elusive. Here, we developed a novel BCL6 small molecule inhibitor, WK369, which exhibits excellent anti-ovarian cancer bioactivity, induces cell cycle arrest and causes apoptosis. WK369 effectively inhibits the growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer without obvious toxicity in vitro and in vivo. meanwhile, WK369 can prolong the survival of ovarian cancer-bearing mice. It is worth noting that WK369 also has significant anti-tumor effects on cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Mechanistic studies have shown that WK369 can directly bind to the BCL6-BTB domain and block the interaction between BCL6 and SMRT, leading to the reactivation of p53, ATR and CDKN1A. BCL6-AKT, BCL6-MEK/ERK crosstalk is suppressed. As a first attempt, our study demonstrates that targeting BCL6 may be an effective approach to treat ovarian cancer and that WK369 has the potential to be used as a candidate therapeutic agent for ovarian cancer.
Keywords: BCL6, Ovarian cancer, BTB domain, Metastasis
