ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):569-584. doi:10.7150/ijbs.89291 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MAPK1 Mediates MAM Disruption and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetic Kidney Disease via the PACS-2-Dependent Mechanism
1. Kidney Disease Center, the First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease Prevention and Control Technology, Hangzhou, China.
3. Institute of Nephrology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
4. Zhejiang Clinical Research Center of Kidney and Urinary System Disease, Hangzhou, China.
5. Department of nephrology, Hangzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China.
6. Department of Nephrology, The Children's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China.
7. Department of Molecular Medicine & Pathology, School of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Medical & Health Sciences, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand.
8. Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Cancer Molecular Cell Biology, Life Sciences Institute, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
9. Department of Biophysics, and Kidney Disease Center of the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China.
10. MOE Key Laboratory for Biosystems Homeostasis & Protection and Innovation Center for Cell Signaling Network, Life Sciences Institute, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
# Equal contribution to the work.
Abstract
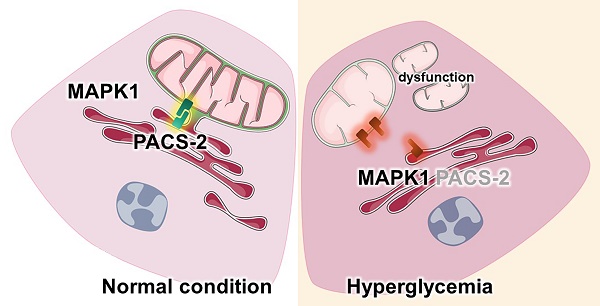
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Mitochondrial dysfunction in renal tubules, occurring early in the disease, is linked to the development of DKD, although the underlying pathways remain unclear. Here, we examine diabetic human and mouse kidneys, and HK-2 cells exposed to high glucose, to show that high glucose disrupts mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) and causes mitochondrial fragmentation. We find that high glucose conditions increase mitogen-activated protein kinase 1(MAPK1), a member of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway, which in turn lowers the level of phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (PACS-2), a key component of MAM that tethers mitochondria to the ER. MAPK1-induced disruption of MAM leads to mitochondrial fragmentation but this can be rescued in HK-2 cells by increasing PACS-2 levels. Functional studies in diabetic mice show that inhibition of MAPK1 increases PACS-2 and protects against the loss of MAM and the mitochondrial fragmentation. Taken together, these results identify the MAPK1-PACS-2 axis as a key pathway to therapeutically target as well as provide new insights into the pathogenesis of DKD.
Keywords: diabetic kidney disease, mitochondria, mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane, MAPK1, PACS-2
