10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):718-732. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85471 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LncRNA CRNDE Drives the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by inducing the Immunosuppressive Niche
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China.
2. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China.
3. Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Hefei, Anhui, China.
4. Anhui Provincial Clinical Research Center for Hepatobiliary Diseases, Hefei, Anhui, China.
#Lead contact.
*These authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
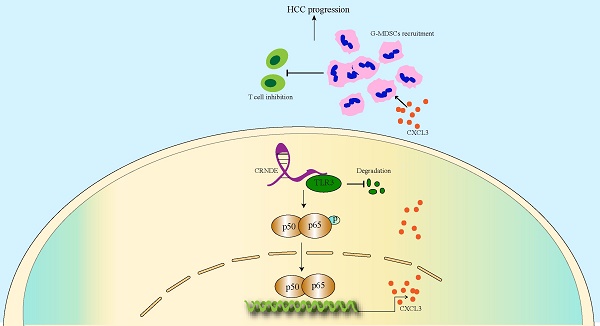
As a crucial protumorigenic long noncoding RNA, colorectal tumor differential expression (CRNDE) has been confirmed to facilitate the progression of various cancers. However, its role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is still unclear. Here we determined that CRNDE was upregulated in HCC samples and that CRNDE-positive cells were predominantly enriched in malignant tumor cells. In vivo functional assays revealed that CRNDE-induced tumor cells supported HCC progression, recruited abundant granulocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs) and restricted the infiltration of T cells. In terms of mechanisms, CRNDE bound with Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and activated NF-κB signaling to increase the secretion of c-x-c motif chemokine ligand 3 (CXCL3). CRNDE knockdown could significantly suppress the accumulation of G-MDSCs and enhance the infiltration of T cells in the TME of HCC in vivo. Taken together, our study reveals the CRNDE-NF-κB-CXCL3 axis plays a crucial role in driving the immunosuppressive niche to facilitate HCC progression by recruiting G-MDSCs.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Colorectal tumor differential expression, Tumor microenvironment, Myeloid-derived suppressor cell, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact