10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):784-800. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82003 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of the HMGB1/RAGE axis protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress
1. ENT institute and Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Eye & ENT Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology and MOE Frontiers Center for Brain Science, Fudan University, Shanghai 200031, China; NHC Key Laboratory of Hearing Medicine (Fudan University), Shanghai 200031, China.
2. Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
3. The Institutes of Brain Science and the Collaborative Innovation Center for Brain Science, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
4. Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
Abstract
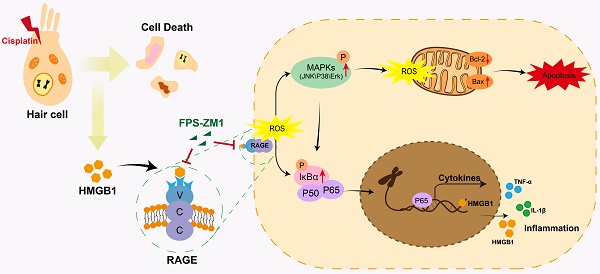
As an anti-tumor drug widely used in the clinic, cisplatin is limited by its ototoxic side effects associated with various factors, including inflammatory responses. Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts (RAGE) recognizes damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and promotes stress and inflammation. This study intended to determine the potential behavior of the HMGB1/RAGE axis after cisplatin injury and whether it has a protective effect after inhibiting this pathway. We used FPS-ZM1, a RAGE inhibitor, to modulate the axis of HMGB1/RAGE in neonatal mouse cochlear explants and C57BL/6 mice in vivo. Apoptosis was identified by Annexin V-FITC/PI assay, Cleaved Caspase-3, and TUNEL staining. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was assessed by MitoSOX Red and CellROX Green assay. The expression of proteins associated with the HMGB1/RAGE axis and apoptosis was observed by western blotting. The expression of inflammatory cytokines was evaluated by qPCR. The protective effect of HMGB1/RAGE knockdown was also assessed on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. These results demonstrated that cisplatin could activate the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in cochlear hair cells and release inflammatory factors. Pretreatment with FPS-ZM1 alleviated cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in vivo and in vitro. Knocking down HMGB1 and RAGE achieved specific protective effects. Altogether, inhibiting HMGB1/RAGE axis can reverse the increase of ROS accumulation, the activation of apoptosis, and the production of inflammatory reactions after cisplatin injury. FPS-ZM1 could resist the ototoxicity of cisplatin by suppressing the HMGB1/RAGE signal pathway, and it may be considered the new otoprotective potential strategy for hearing loss.
Keywords: Cisplatin, Hair cells, FPS-ZM1, HMGB1, RAGE, Ototoxicity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact