10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(6):701-711. doi:10.7150/ijbs.17534 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Eupafolin Exhibits Potent Anti-Angiogenic and Antitumor Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. General Surgery department, the fourth affiliated hospital of China medical university, Shenyang, China;
2. Infectious disease department, Shengjing hospital of China medical university, Shenyang, China.
Abstract
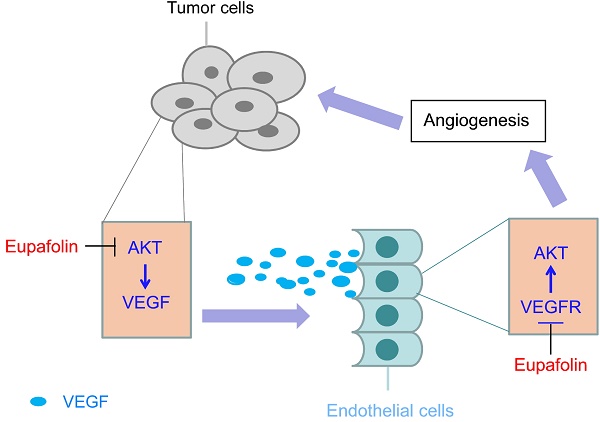
Eupafolin is a flavonoid extracted from the common sage herb which has been used in China as traditional medicine. Previous studies had reported that eupafolin had antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and antitumor effects. However, the function and the mechanism of eupafolin to exert its antitumor activity, especially its effect on tumor angiogenesis, have not been elucidated. Herein, we showed that eupafolin significantly inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced cell proliferation, migration and tube formation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a dose-dependent manner. Meanwhile, the new blood microvessels induced by VEGF in the matrigel plug were also substantially suppressed by eupafolin. The results of HCC xenograft experiments demonstrated eupafolin remarkably inhibited tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis in vivo, suggesting the antitumor activity exerted by eupafolin was closely correlated with its potency on tumor angiogenesis. Mechanism investigations revealed that eupafolin significantly blocked VEGF-induced activation of VEGFR2 in HUVEC cells as well as its downstream signaling pathway. In addition to the effect on endothelial cells, through inhibiting Akt activity in tumor cells, VEGF secretion in HepG2 was dramatically decreased after eupafolin treatment. Our study was the first to report the activity of eupafolin against tumor angiogenesis as well as the underlying mechanism by which eupafolin to exert its anti-angiogenic activity.
Keywords: Eupafolin, tumor angiogenesis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact