10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(12):1696-1708. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27774 This issue Cite
Research Paper
GLP-1 treatment protects endothelial cells from oxidative stress-induced autophagy and endothelial dysfunction
1. Clinical Laboratory, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, 510080, People's Republic of China.
2. Guangzhou Institute of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Guangzhou, 510660, People's Republic of China.
3. Institute of Biotherapy, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510515, People's Republic of China.
4. Dermatology Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510091, People's Republic of China.
5. ShenZhen Hospital, Southern Medical University, ShenZhen 518101, People's Republic of China.
6. Technology Center, Guangdong Vitalife Bio-tech Co.,LTD, FoShan, 528200, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
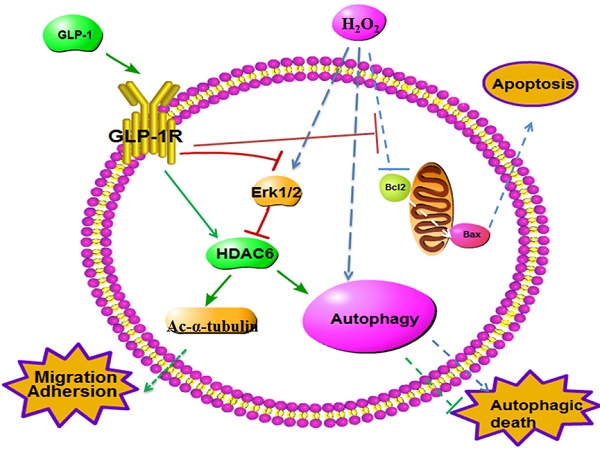
Endothelial dysfunction and excessively stimulated autophagy, often caused by oxidant injury or inflammation, will lead to atherosclerosis development and progression in diabetes. The aim of this study is to investigate the protective effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) treatment on preventing oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and excessively stimulated autophagy. Treatment of endothelial cells with GLP-1 significantly attenuated oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and autophagy, which was associated with the reduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. These protective effects of GLP-1 were likely mediated by reducing phosphorylation of ERK1/2. We further demonstrated that GLP-1 treatment could reverse downregulation of epigenetic factor histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), a downstream molecular of the EKR1/2, induced by oxidant injury. In conclusion, our results suggest that GLP-1 produces a protective effect on endothelial cells from oxidant injury by preventing endothelial dysfunction and autophagy, which may be dependent on restoring HDAC6 through a GLP-1R-ERK1/2-dependent manner.
Keywords: oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, GLP-1, autophagy, HDAC6

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact