10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(4):800-811. doi:10.7150/ijbs.30356 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dendropanax morbifera Ameliorates Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis via TGF-β1/Smads Pathways
1. School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, 2066, Seobu-ro, Suwon, 16419, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Republic of Korea
3. College of Pharmacy and Institute of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Hanyang University, Ansan, Gyeonggi-do 15588, Republic of Korea
4. McLaughlin Centre for Population Health Risk Assessment, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
5. Comparative Biomedicine Research Branch, Division of Translational Science, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10408, Republic of Korea
Abstract
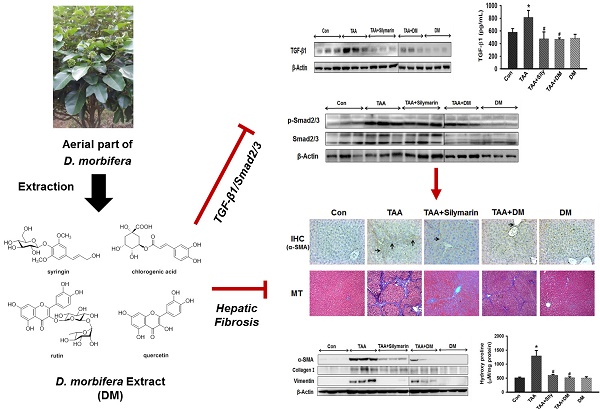
Hepatic fibrosis, characterized by persistent deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, occurs in most types of chronic liver disease. The prevention of liver damage using extract of Dendropanax morbifera has been widely studied, but its molecular mechanism on the therapeutic efficacy of hepatic fibrosis is unclear. The aim of this study was to assess whether aquatic extract (DM) of D. morbifera ameliorates thioacetamide (TAA)-induced hepatic fibrosis. Hepatic fibrosis was induced by an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection (150 mg/kg, twice per week) of TAA for 6 weeks. DM (50 mg/kg/day) or silymarin (50 mg/kg/day) was administered daily for 6 weeks. DM markedly reduced serum AST, ALT, ALP, and r-GTP in TAA-treated rats. DM significantly ameliorated the total glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) activity in TAA-treated rats. In particular, DM significantly reduced expression of α-SMA, type I collagen, vimentin, TGF-β1 and p-Smad2/3 in hepatic fibrosis rats. The protective effects of DM on progression of hepatic fibrosis were clearly shown by detecting 4-hydroxyproline concentration and histopathological examination in the liver. Therefore, our data suggest that DM dramatically prevented hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting oxidative stress and the TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathways.
Keywords: hepatic fibrosis, thioacetamide, TGF-β1, α-smooth muscle actin, Dendropanax morbifera

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact