10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(2):751-764. doi:10.7150/ijbs.83205 This issue Cite
Review
Molecular Modulators and Receptors of Selective Autophagy: Disease Implication and Identification Strategies
State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, Macau, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this paper.
Abstract
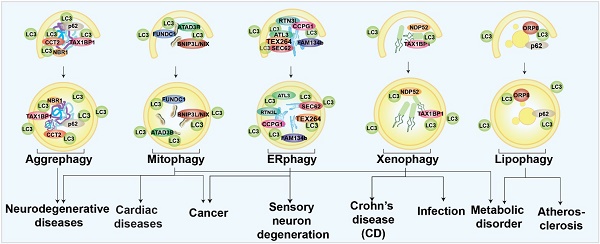
Autophagy is a highly conserved physiological process that maintains cellular homeostasis by recycling cellular contents. Selective autophagy is based on the specificity of cargo recognition and has been implicated in various human diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Selective autophagy receptors and modulators play key roles in this process. Identifying these receptors and modulators and their roles is critical for understanding the machinery and physiological function of selective autophagy and providing therapeutic value for diseases. Using modern researching tools and novel screening technologies, an increasing number of selective autophagy receptors and modulators have been identified. A variety of Strategies and approaches, including protein-protein interactions (PPIs)-based identification and genome-wide screening, have been used to identify selective autophagy receptors and modulators. Understanding the strengths and challenges of these approaches not only promotes the discovery of even more such receptors and modulators but also provides a useful reference for the identification of regulatory proteins or genes involved in other cellular mechanisms. In this review, we summarize the functions, disease association, and identification strategies of selective autophagy receptors and modulators.
Keywords: selective autophagy, autophagy, screening technology, protein-protein interaction, genome-wide screening

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact