10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(8):868-878. doi:10.7150/ijbs.12045 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptor Trafficking and Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cell Permeability by Rab5 GTPase
1. Institute of Respiratory Diseases, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China
2. Department of Cardiology, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China
3. Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Medical College of Georgia, Georgia Regents University, Augusta 30912, USA
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
# Current address: Intensive Care Unit, Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang 621000, China
Abstract
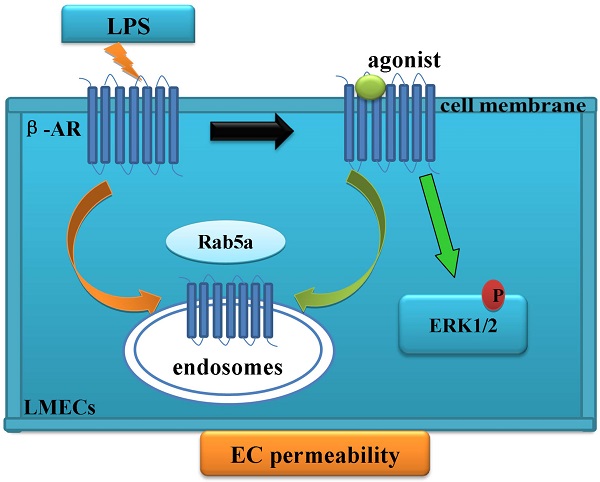
Rab5 GTPase modulates the trafficking of the cell surface receptors, including G protein-coupled β-adrenergic receptors (β-ARs). Here, we have determined the role of Rab5 in regulating the internalization of β-ARs in lung microvascular endothelial cells (LMECs) and in maintaining the integrity and permeability of endothelial cell barrier. Our data demonstrate that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment disrupts LMEC barrier function and reduces the cell surface expression of β-ARs. Furthermore, the activation of β-ARs, particularly β2-AR, is able to protect the LMEC permeability from LPS injury. Moreover, siRNA-mediated knockdown of Rab5 inhibits both the basal and agonist-provoked internalization of β-ARs, therefore, enhancing the cell surface expression of the receptors and receptor-mediated ERK1/2 activation. Importantly, knockdown of Rab5 not only inhibits the LPS-induced effects on β-ARs but also protects the LMEC monolayer permeability. All together, these data provide strong evidence indicating a crucial role of Rab5-mediated internalization of β-ARs in functional regulation of LMECs.
Keywords: lung, microvascular endothelial cell, Rab5, β-adrenergic receptor, internalization, trafficking, permeability, lipopolysaccharide, small interfering RNA

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact