10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(11):1314-1324. doi:10.7150/ijbs.11344 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CELF1 is Up-Regulated in Glioma and Promotes Glioma Cell Proliferation by Suppression of CDKN1B
Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou 310022, Zhejiang Province, P.R.C
* Liang Xia, Caixing Sun and Qinglin Li contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
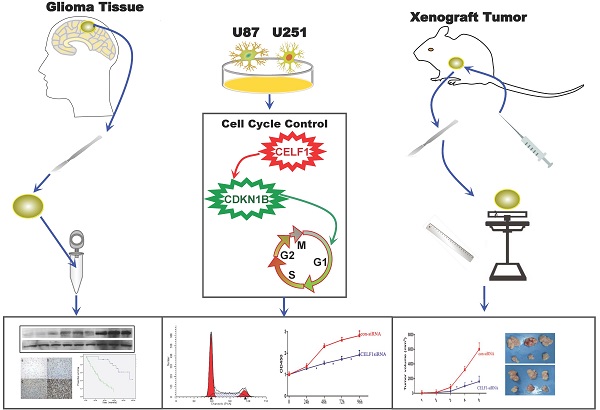
BACKGROUND: As a member of the CELF family, CELF1 (CUG-binding protein 1, CUGBP1) is involved in cardiac and embryonic development, skeletal muscle differentiation and mammary epithelial cell proliferation. CELF1 is also observed in many kinds of cancer and may play a great role in tumorigenesis and deterioration. However, the expression and mechanism of its function in human glioma remain unclear.
METHODS: We examined CELF1 expression in 62 glioma patients by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. The association between the expression of CELF1 protein and clinicopathological characteristics was analysed using SPSS 17.0. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Small-interfering RNA was utilised to specifically knockdown CELF1 mRNA in U87 and U251 cells. Cell proliferation, cell cycle and cell apoptosis were tested by Cell Counting Kit-8 and flow cytometry. The expression of cell cycle-related gene CDKN1B was investigated by Western blot. The interactions between CELF1 and CDKN1B were detected with immune co-precipitation. Subcutaneous tumour models were used to study the effect of CELF1 on the growth of glioma cells in vivo.
RESULTS: Our results showed that CELF1 protein was frequently up-regulated in human glioma tissues. The expression level of this protein was positively correlated with glioma World Health Organisation grade and inversely correlated with patient survival (P < 0.05). Knockdown of CELF1 inhibited the glioma cell cycle process and proliferation potential, possibly by down-regulating its target, CDKN1B protein.
CONCLUSIONS: Results indicated that CELF1 may be a novel independent prognostic predictor of survival for glioma patients. It may promote glioma cell proliferation and cell cycle process during glioma carcinogenesis.
Keywords: CELF1, Glioma, Prognosis, Proliferation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact