10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(5):558-568. doi:10.7150/ijbs.11051 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Direct Reprogramming of Human Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells by OCT4 and Application in Repairing of Cerebral Ischemia Damage
1. The Stem Cell and Biomedical Material Key Laboratory of Jiangsu Province (the State Key Laboratory Incubation Base), Suzhou, Jiangsu Province, P.R.China.
2. Jiangsu Institute of Clinical Immunology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, P.R.China.
3. The Reproductive and Genetic Center, the Municipal Hospital of Suzhou, Suzhou, Jiangsu Province, P.R.China.
*Co-First authors.
Abstract
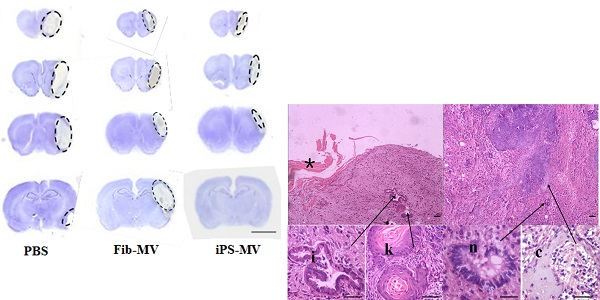
Amniotic fluid stem cells (AFSCs) are a type of fetal stem cell whose stemness encompasses both embryonic and adult stem cells, suggesting that they may be easily and efficiently reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). To further simplify the reprogramming process, the creation of AFSC-derived iPSCs using a single factor is desirable. Here we report the generation of one-factor human AFSC-iPSCs (AiPSCs) from human AFSCs by ectopic expression of the transcription factor OCT4. Just like human embryonic stem cells, AiPSCs exhibited similar epigenetic status, global gene expression profiles, teratoma formation and in vitro & in vivo pluripotency. Our results indicate that the OCT4 is necessary and sufficient to directly reprogram human AFSCs into pluripotent AiPSCs. Moreover, reflecting the similar memory characteristics of AFSCs and neural stem cells, we show that AiPSC membrane-derived vesicles (MVs) repair cerebral ischemia damage. We anticipate that the successful generation of one-factor AiPSCs will facilitate the creation of patient-specific pluripotent stem cells without the need for transgenic expression of oncogenes. Moreover, MVs from tissue-specific AiPSCs have potential in tissue repair, representing a novel application of iPSCs.
Keywords: Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSCs), Amniotic fluid stem cell (AFSCs) & Membrane-derived vesicle (MV).

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact