10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(6):654-666. doi:10.7150/ijbs.24765 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Incorporation of DDR2 clusters into collagen matrix via integrin-dependent posterior remnant tethering
1. Jiangsu key lab of Drug Screening, Jiangsu key lab of Drug Discovery for Metabolic Disease, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China;
2. Research Center for High Altitude Medicine, Qing Hai University, Xining 810001, China
3. Institute of Virology, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, 325000, China;
4. Innate Gene Inc., Beijing 100085, China.
Abstract
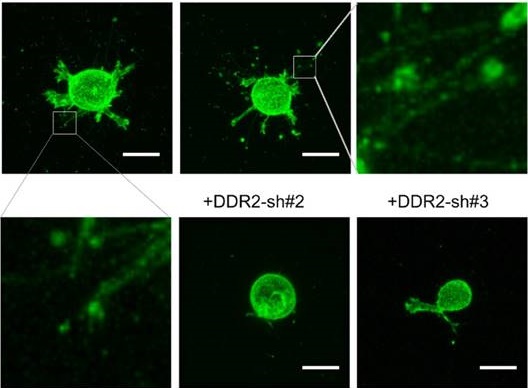
Cell-matrix interactions play critical roles in cell adhesion, tissue remodeling and cancer metastasis. Discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) is a collagen receptor belonging to receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. It is a powerful regulator of collagen deposition in the extracellular matrix (ECM). Although the oligomerization of DDR extracellular domain (ECD) proteins can affect matrix remodeling by inhibiting fibrillogenesis, it is still unknown how cellular DDR2 is incorporated into collagen matrix. Using 3-dimentional (3D) imaging for migrating cells, we identified a novel mechanism that explains how DDR2 incorporating into collagen matrix, which we named as posterior remnant tethering. We followed the de novo formation of these remnants and identified that DDR2 clusters formed at the retracting phase of a pseudopodium, then these clusters were tethered to fibrillar collagen and peeled off from the cell body to generate DDR2 containing posterior remnants. Inhibition of β1-integrin or Rac1 activity abrogated the remnant formation. Thus, our findings unveil a special cellular mechanism for DDR2 clusters incorporating into collagen matrix in an integrin-dependent manner.
Keywords: DDR2, integrin, collagen, posterior remnants.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact