10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(12):1678-1685. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27896 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis Based on Human Signaling Networks and Stem Cell Expression Data
1. College of Bioinformatics Science and Technology, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
2. Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
3. Dean's Office, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
4. Department of general surgery, General Hospital of Heilongjiang Province Land Reclamation Bureau, 150088, Harbin, China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
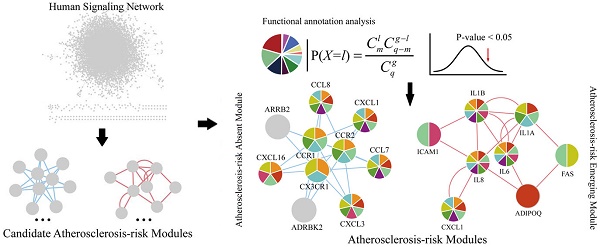
Atherosclerosis is a common and complex disease, whose morbidity increased significantly. Here, an integrated approach was proposed to elucidate systematically the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis from a systems biology point of view. Two weighted human signaling networks were constructed based on atherosclerosis related gene expression data of stem cells. Then, 37 candidate Atherosclerosis-risk Modules were detected using four kinds of permutation tests. Five Atherosclerosis-risk Modules (three Absent Modules and two Emerging Modules) enriched in functions significantly associated with disease genes were identified and verified to be associated with the maintenance of normal biological process and the pathogenesis and development of atherosclerosis. Especially for Atherosclerosis-risk Emerging Module P96, it could distinguish between normal and disease samples by Supporting Vector Machine with the average expression value of the module as classification feature. These identified modules and their genes may act as potential atherosclerosis biomarkers. Our study would shed light on the signal transduction of atherosclerosis, and provide new insights to its pathogenesis from the perspective of stem cells.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, stem cell, human signaling network, module, expression data

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact