10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(3):460-470. doi:10.7150/ijbs.39016 This issue Cite
Review
Mucosal-Associated Invariant T cell in liver diseases
1. Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, 230032, China;
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Fuyang Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Fuyang, Anhui 236000, P.R. China;
3. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, 230032, China.
Abstract
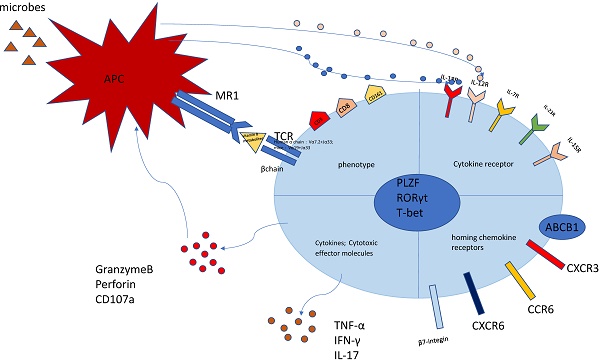
Mucosal-associated invariant T cells (MAIT cells) are a new population of innate immune cells, which are abundant in the liver and play complex roles in various liver diseases. In this review, we summarize MAIT cells in the liver diseases in recent studies, figure out the role of MAIT cells in various liver disease, including Alcoholic liver disease, Non-alcoholic liver disease, Autoimmune liver diseases, Viral hepatitis and Liver Cancer. Briefly, MAIT cells are involved in anti-bacteria responses in the alcoholic liver diseases. Besides, the activated MAIT cells promote the liver inflammation by secreting inflammatory cytokines and produce regulatory cytokines, which induces anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization. MAIT cells participate in the liver fibrosis via enhancing hepatic stellate cell activation. In viral hepatitis, MAIT cells exhibit a flawed and exhausted phenotype, which results in little effect on controlling the virus and bacteria. In liver cancer, MAIT cells indicate the disease progression and the outcome of therapy. In summary, MAIT cells are attractive biomarkers and therapeutic targets for liver disease.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease, autoimmune liver disease, liver cancer, MAIT cells, non-alcoholic liver disease

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact