10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(7):1207-1217. doi:10.7150/ijbs.39779 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Therapeutic Targeting of CDK7 Suppresses Tumor Progression in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
1. Department of Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China
2. Department of Pediatric Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China
3. RNA Biomedical Institute, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China
4. Key Laboratory of Stem Cells and Tissue Engineering (Sun Yat-Sen University), Ministry of Education, Guangzhou 510080, China
#These authors contribute equally to this study.
Abstract
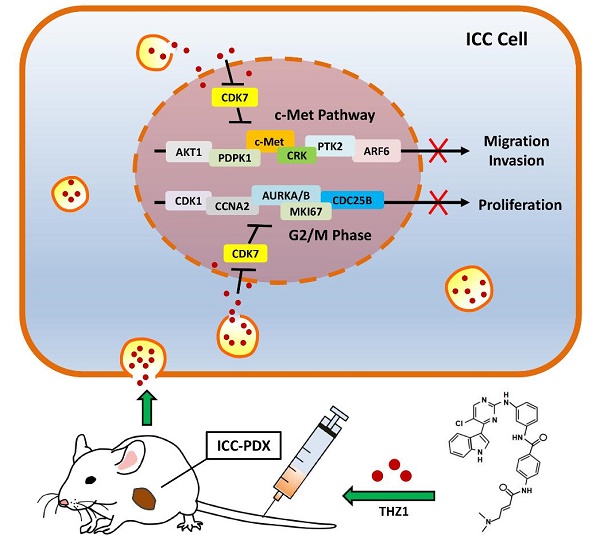
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is a lethal malignancy with high mortality and lack of effective therapeutic targets. Here, we found that expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) was significantly associated with higher tumor grade and worse prognosis in 96 ICC specimens. Depletion of CDK7 significantly inhibited cell growth, induced a G2/M cell cycle arrest, and reduced the migratory and invasive potential in ICC cells. Subsequent experiments demonstrated that ICC cells were highly sensitive to the CDK7 inhibitor THZ1. A low concentration of THZ1 markedly inhibited cell growth, cell cycle, migration, and invasion in ICC cell lines. RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis revealed that THZ1 treatment decreased the levels of massive oncogene transcripts, particularly those associated with cell cycle and cell migration. Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis confirmed that transcription of oncogenes involved in cell cycle regulation (AURKA, AURKB, CDC25B, CDK1, CCNA2, and MKI67) and the c-Met pathway (c-Met, AKT1, PTK2, CRK, PDPK1, and ARF6) was selectively repressed by THZ1. In addition, THZ1 exhibited significant anti-tumor activity in a patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model of ICC, without causing detectable side effects.
Keywords: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, Cyclin-dependent Kinase 7, THZ1, Cell cycle, c-Met

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact