10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(5):1289-1301. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56933 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Enforced expression of miR-92b blunts E. coli lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/β-catenin pathway via targeting PTEN
1. College of Veterinary Medicine, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming 650201, Yunnan, People's Republic of China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, People's Republic of China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
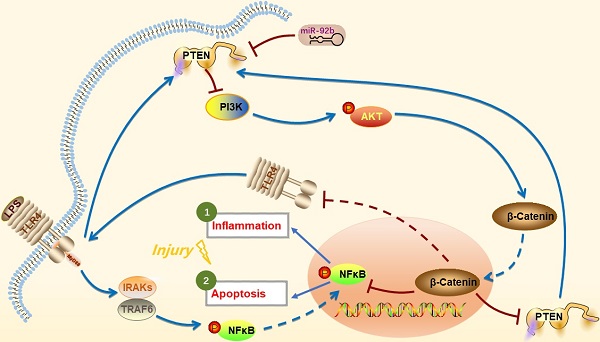
Endometritis is a reproductive disorder characterized by an inflammatory response in the endometrium, which causes significant economic losses to the dairy farming industry. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are implicated in the inflammatory response and immune regulation following infection by pathogenic bacteria. Recent miRNA microarray analysis showed an altered expression of miR-92b in cows with endometritis. In the present study, we set out to investigate the regulatory mechanism of miR-92b in endometritis. Here, qPCR results first validated that miR-92b was down-regulated during endometritis. And then, bovine endometrial epithelial cells (BEND cells) stimulated by high concentration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were employed as an in vitro inflammatory injury model. Our data showed that overexpression of miR-92b significantly suppressed the activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor-κB (NF‐κB) in LPS-stimulated BEND cells, thereby reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines release and inhibiting cell apoptosis. Looking into the molecular mechanisms of regulation of inflammatory injury by miR-92b, we observed that overexpression of miR-92b restrained TLR4/NF‐κB by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT)/β-catenin pathway. Furthermore, the luciferase reporter assay suggested that miR-92b targeted inhibition of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), an inhibitor of the PI3K/AKT/β-catenin pathway. Importantly, in vivo experiments confirmed that up-regulation of miR-92b attenuated the pathological injury in an experimental murine model of LPS-induced endometritis. Collectively, these findings show that enforced expression of miR-92b alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/β-catenin pathway via targeting PTEN, suggesting a potential application for miR-92b-based therapy to treat endometritis or other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: endometritis, miR-92b, inflammation, apoptosis, PI3K/AKT

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact