10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(5):1328-1338. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58786 This issue Cite
Review
Potential of exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic carriers for doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
1. Department of Cardiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, China.
2. Department of Immunology, Basic Medicine School, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, China.
3. Institute for Translational Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266021, China.
4. Department of Cardiac Ultrasound, The Affiliated hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, China.
5. Department of Cardiology, The Affiliated Cardiovascular Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266032, China.
6. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, The Affiliated Cardiovascular Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this paper.
Abstract
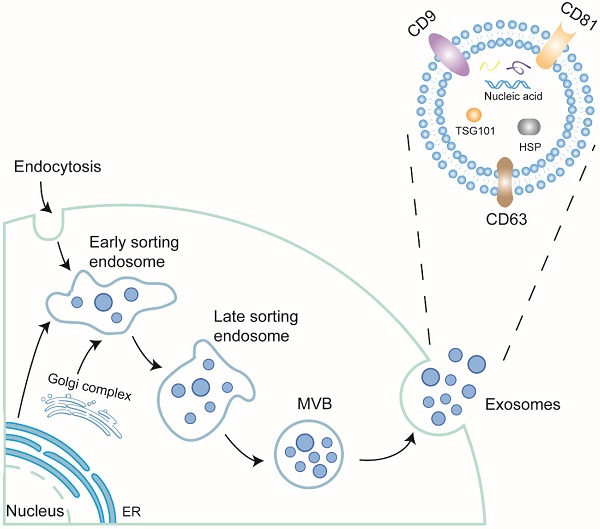
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a kind of representative anthracyclines. It has greatly prolonged lifespan of cancer patients. However, a long course of DOX chemotherapy could induce various forms of deaths of cardiomyocytes, such as apoptosis, pyroptosis and ferroptosis, contributing to varieties of cardiac complications called cardiotoxicity. It has become a major concern considering the large number of cancer patients' worldwide and increased survival rates after chemotherapy. Exosomes, a subgroup of extracellular vesicles (EVs), are secreted by nearly all cells and consist of lipid bilayers, nucleic acids and proteins. They can serve as mediators between intercellular communication via the transfer of bioactive molecules from secretory to recipient cells, modulating multiple pathophysiological processes. It has been proven that exosomes in body fluids can serve as biomarkers for doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC). Moreover, exosomes have attracted considerable attention because of their capacity as carriers of certain proteins, genetic materials (miRNA and lncRNA), and chemotherapeutic drugs to decrease the dosage of DOX and alleviate cardiotoxicity. This review briefly describes the characteristics of exosomes and highlights their clinical application potential as diagnostic biomarkers and drug delivery vehicles for DIC, thus providing a strategy for addressing it based on exosomes.
Keywords: doxorubicin, cardiotoxicity, exosome, biomarker, delivery vehicles

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact